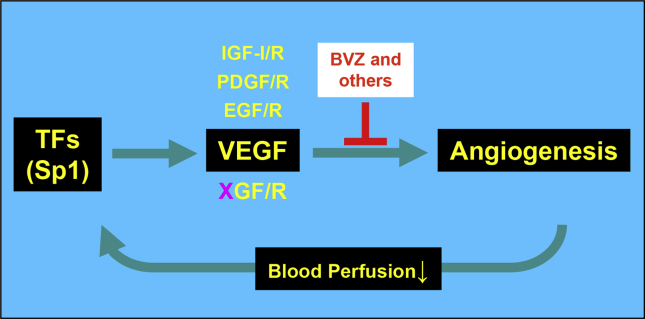
Figure 3.
VEGF inhibitors resistance model. The use of a VEGF neutralizing antibody (“BVZ” or others) decreases tumor angiogenesis of and reduces blood perfusion to tumor tissues. Increased hypoxia and other changes aggravate the stressful microenvironment in the tumor. The tumor cells counteract by inducing the expression of critical transcription factors (“TFs”) like Sp1, which upregulates VEGF expression and renders BVZ resistance. Permanent resistance to BVZ occurs when other functionally redundant factors, e.g., IFG-I/R, PDGF/R, EGF/R and other unknown factors (“XGF/R”), are also unregulated by the increased expression of Sp1, which is initiated by the treatment of the VEGF neutralizing antibody.