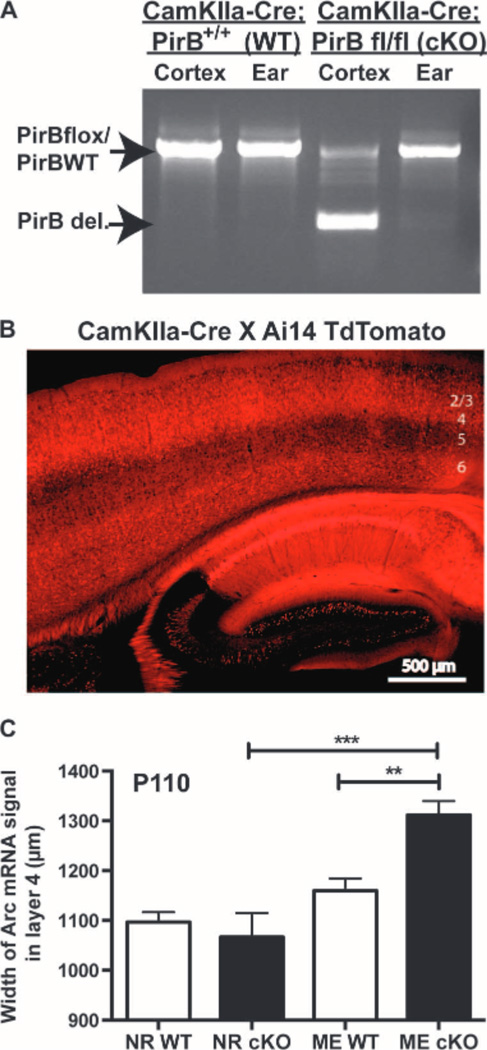
Fig. 3.
Cre-mediated deletion of PirB from forebrain excitatory neurons enhances adult OD plasticity. (A) Genotyping of samples from ear and cerebral cortex from P100 CamKIIa-Cre; PirB flox/flox (cKO) or CamKIIa-Cre; PirB WT (wild type), showing deletion of floxed PirB in cortex but not ear. (B) CamKIIa-Cre; PirB flox/+ breeders were crossed with the Ai14 TdTomato reporter line, generating red fluorescence in the presence of Cre. Sagittal section through visual cortex (layers indicated at right) and hippocampus of a P30 mouse shows Cre present in pyramidal neurons. (C) Graphs of width of L4 region activated by stimulation of ipsilateral (open) eye in visual cortex, assessed using Arc mRNA induction. Deletion of PirB from forebrain excitatory neurons increases open-eye expansion in adult mice after ME from P100 to P110. NRWT: n = 5 mice versus NRcKO: n = 4, P = 0.91. MEWT: n = 8 mice versus MEcKO: n=5, P = 0.006. NR versus MEWT: P = 0.39, NR versus MEcKO: P = 0.0002,by two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test.**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001.