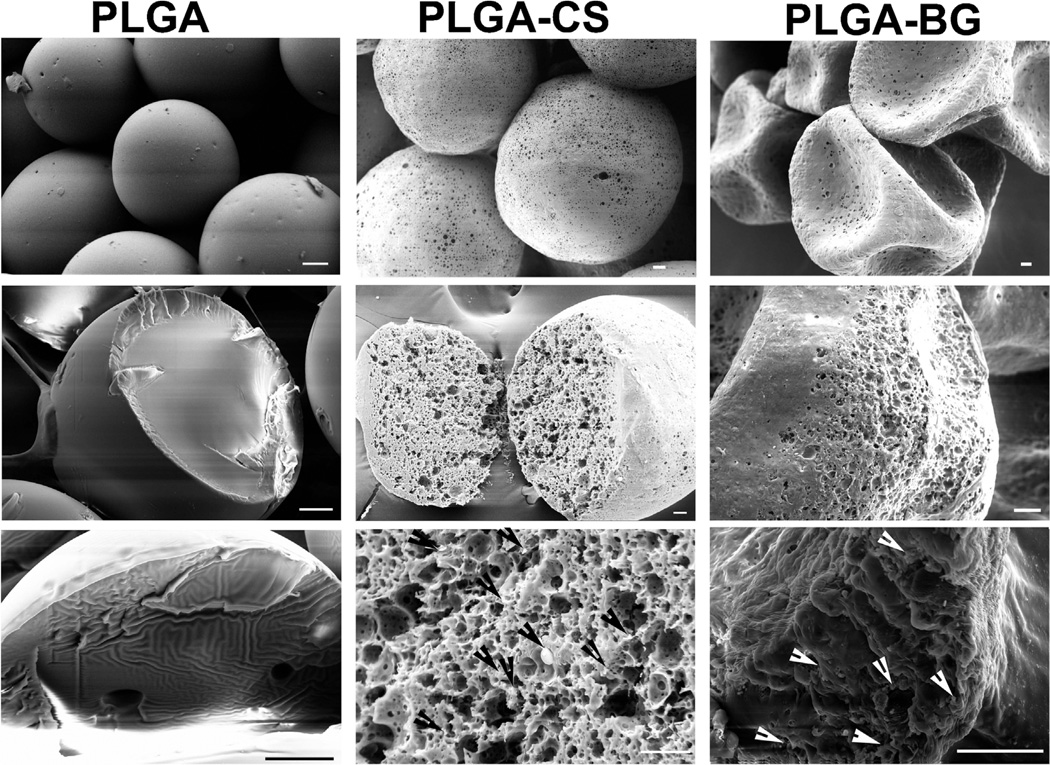
Figure 1.
Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of microspheres prior to the fabrication of scaffolds. The images in the top panel from each column demonstrate the morphology of the surface; the middle and the lower panels demonstrate the cross section of cryofractured microspheres. PLGA microspheres had smooth surfaces, whereas the microspheres with encapsulated CS or bioactive glass had porous surfaces. The PLGA-BG microspheres had the structure of a deflated soccer ball after lyophilization. The arrows in the lower panel in PLGA-CS and PLGA-BG point to the chondroitin sulfate and bioactive glass particles deposited inside the microspheres. Scale bars: 20 µm. PLGA poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid), PLGA-CS poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid-chondroitin sulfate), PLGA-BG (poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-bioactive glass).