Fig 4.
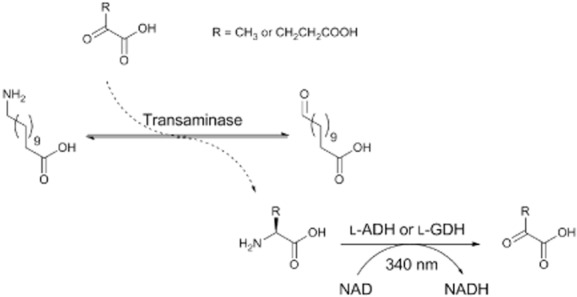
Dehydrogenase-coupled UV assay for transaminase activity. The transaminase catalyzes the transfer of the amine from the 12-aminododecanoic acid to the α-keto acid co-substrate, producing the C12 semialdehyde and alanine or glutamate as a co-product. The dehydrogenase then catalyzes the oxidative deamination of the co-product utilizing a cofactor, NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is concurrently reduced to NADH. Formation of NADH can be detected by UV photospectrometry as a hyperchromic shift at 340 nm.
