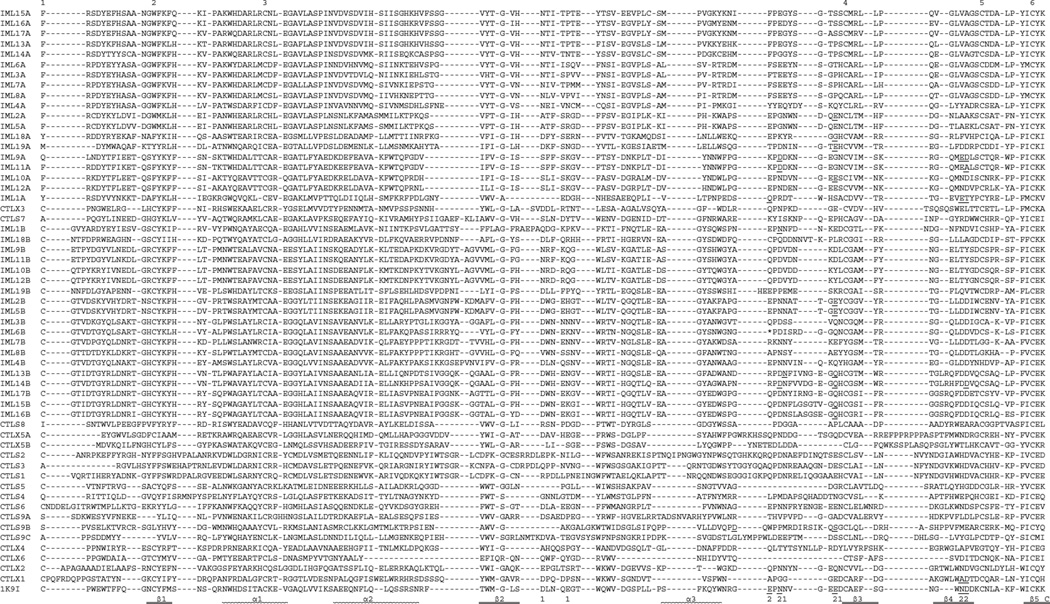
Fig. 5.
Sequence alignment of the M. sexta CTL domains. Based on the domain predictions using SMART, the 56 CTL domain sequences are aligned with that of the rat mannose binding protein (IK9I). For IML-6, the sequence after the stop codon (*, shaded red) also included. In the aligned sequences, ‘EPN’ and ‘QPD’ motifs are highlighted at ‘P’ gray and cyan, respectively. Residues involved in Ca2+ binding in site-1 and −2 (labeled “1” and “2”, respectively) are shaded yellow. Residues involved in carbohydrate binding (based on the models in Fig. 6 and data not shown) are highlighted green, with those also binding Ca2+ underlined. Of the six conserved Cys residues, Cys-1 and −2, −3 and −6, −4 and −5 are predicted to form three disulfide bonds in 23 CTL domains. The other 30 CTL domains may lack the bond between Cys-1 and −2 or Cys-4 and −5. In other parts of the sequences, Cys residues (in red font) may form disulfide bridges with other linkage patterns. The SIDPLDVPQGSTAPQRTARHGTEHVM between D and T (shaded pink) in CTL-S4 and LDILRSEG between A and D (shaded pink) in CTL-S9 domain A are removed along with the gaps in the other sequences.