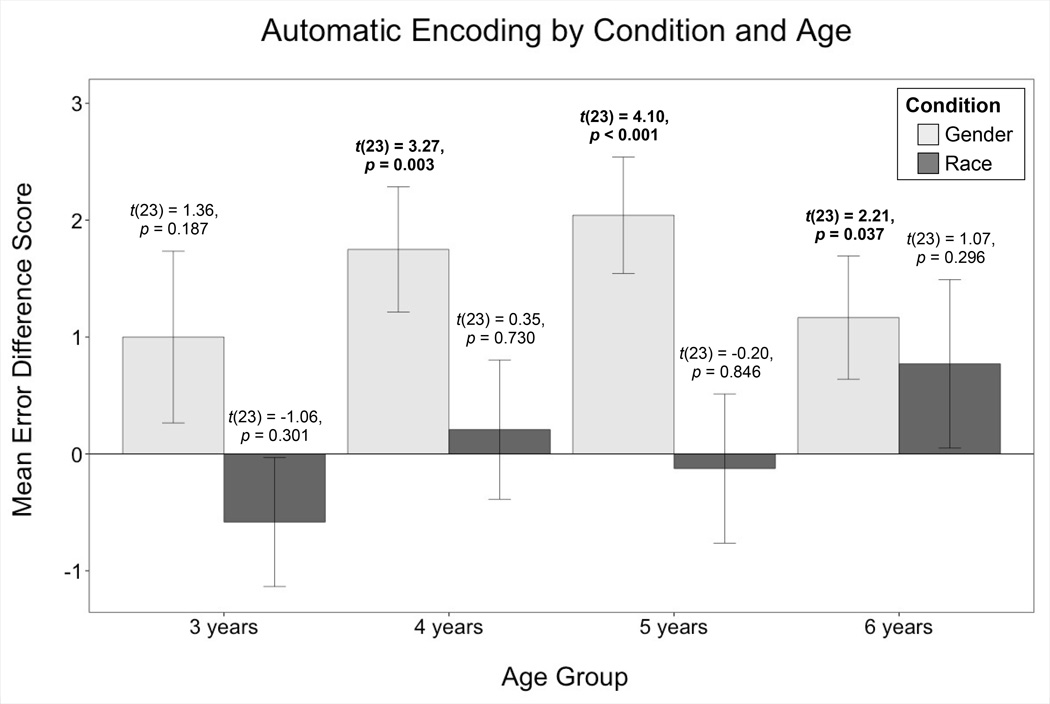
Figure 1.
Mean adjusted error difference scores at each age in each condition. One-sample t-tests to chance (0) appear above each bar in the graph. Error bars depict standard error. Wilcoxon signed rank tests confirmed that children encoded gender as early as four years of age (3 years: W = 63, z = 1.17, p = 0.243; 4 years: W = 150, z = 2.79, p = 0.005; 5 years: W = 191, z = 3.31, p = 0.001; 6 years: W = 98, z = 1.82, p = 0.069), and that no age group showed significant encoding of race (3 years: W = −54, z = −0.95, p = 0.344; 4 years: W = 22, z = 0.33, p = 0.744; 5 years: W = −21, z = −0.35, p = 0.727; 6 years: W = 60, z = 0.97, p = 0.334).