Supplementary Fig. 1.
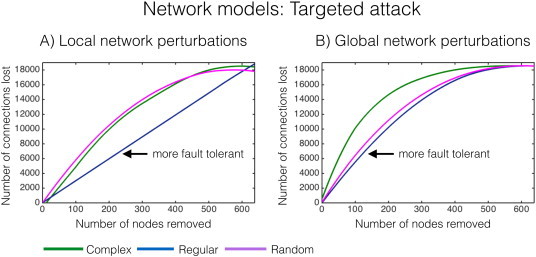
Targeted attack of networks. Network nodes of highest LE (A)and GE (B)were removed iteratively for the complex, regular and random network models in Fig.2, and the subsequent number of surviving connections was counted. A high number of lost connections indicate that the network is fault intolerant, i.e.,the curve in the above graph above is ‘left shifted’, or more in the upper left quadrant. The graphs towards the lower right quadrant are more fault tolerant. A)The regular network is robust to local network perturbations (arrow), whereas in B)both regular and random networks are robust to global network perturbations (arrow).
