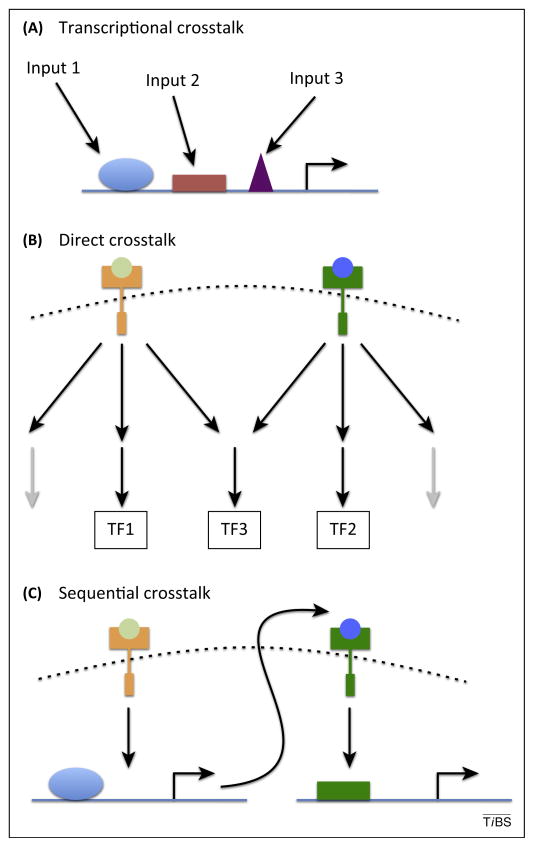
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of crosstalk. Depending on the category of pathways used, communication between pathways can occur at different levels. (A) Integration of transcription factors (blue, red, and purple shapes) at the enhancer level (all pathways). (B) Direct crosstalk between components of the transduction machinery can lead to activation of different transcription factors (TF) and/or the use of different transduction pathways (black arrows represent active transduction pathways, gray arrows represent inactive transduction pathways). This is more likely with increased pathway complexity. (C) Sequential activation of pathways (possible for all pathways). Note that sequential activation of pathways can be difficult to distinguish from simultaneous signaling, depending on the assays and tools used to monitor pathway activity.