Figure 4.
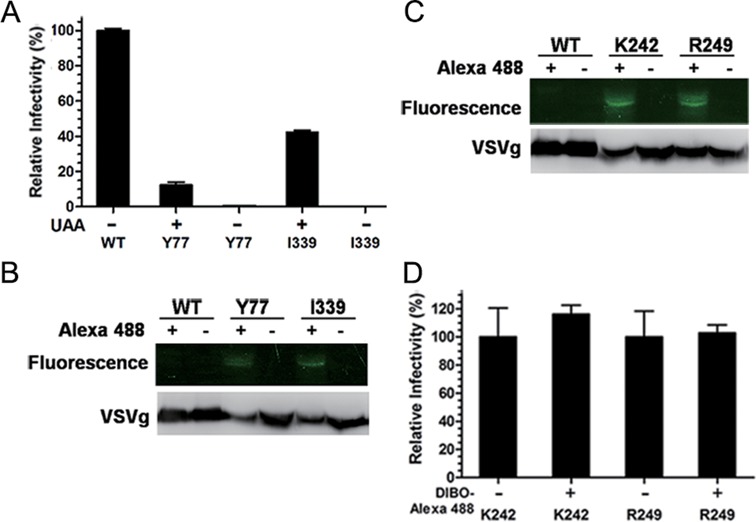
Site-specific display of NAEK on the surface of lentiviral vectors. (A) Test of the infectivity of the lentiviral vector containing NAEK at site Y77 or I339, respectively, by luciferase assay using HeLa cells as the host. The infectivity of lentiviral vectors was quantified by luminescence measurement and normalized to that of the wild-type lentiviral vectors (WT). (B) Verification of NAEK expression on lentiviral vectors by their capability to conjugate with the DIBO-Alexa 488 probe via click reaction, which made NAEK-bearing protein visible by fluorescence upon conjugation with Alexa 488. The wild-type (WT), acting as a negative control, and mutant lentiviral vectors were separately incubated with (+) or without (–) DIBO-Alexa 488 and then analyzed by fluorescence scanning (upper bands) and western blotting (lower bands) via 9% SDS-PAGE. (C) Generation of highly infectious NAEK-containing lentiviral vectors with (+) or without (–) Alexa 488 at site K242 and R249, respectively, which were analyzed by fluorescent scanning (upper bands) and western blotting(lower bands). (D) Characterizations of the infectivity of lentiviral vectors with (+) or without (–) Alexa 488 at site K242 and R249, respectively by luciferase assay. All quantitative data shown are average values with standard deviations from triplicate experiments. These lentiviral vectors produced from the same transfection were split, treated and compared in parallel.
