Figure 7.
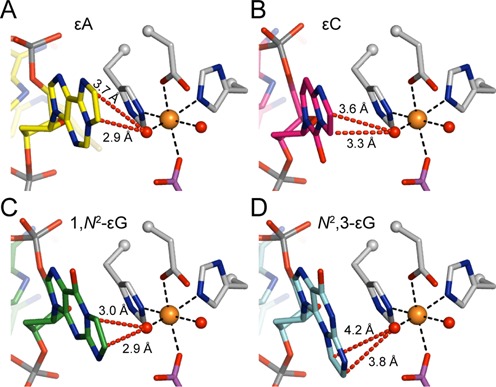
Models of the four etheno lesions in the active site of AlkB. (A) AlkB active site with an εA lesion (yellow carbons, PDB ID: 3O1P), a known good substrate for AlkB, and with the iron(IV)-oxo intermediate modeled (see below). (B–D) Models of AlkB with (B) εC (pink carbons), (C) 1,N2-εG (green carbons), and (D) N2,3-εG (cyan carbons) lesions in the active site. Models of 1,N2-εG and N2,3-εG are based on the crystal structure of εA in AlkB (PDB ID: 3O1P) and the model of εC is based on the crystal structure of 3-methylcytosine (3mC) in AlkB (PDB ID: 3O1M, Supplementary Figure S6). In all panels, selected AlkB amino acid residues are shown in grey, iron-bound succinate in purple, the iron ion as an orange sphere, and iron-bound oxygens (or water molecules) as red spheres. The iron(IV)-oxo intermediate is modeled based on a recent study, with an iron-oxygen distance of 1.62 Å (56). Distances from the iron(IV)-oxo oxygen atom to the exocyclic etheno carbon atoms are shown as red dashed lines.
