Figure 3.
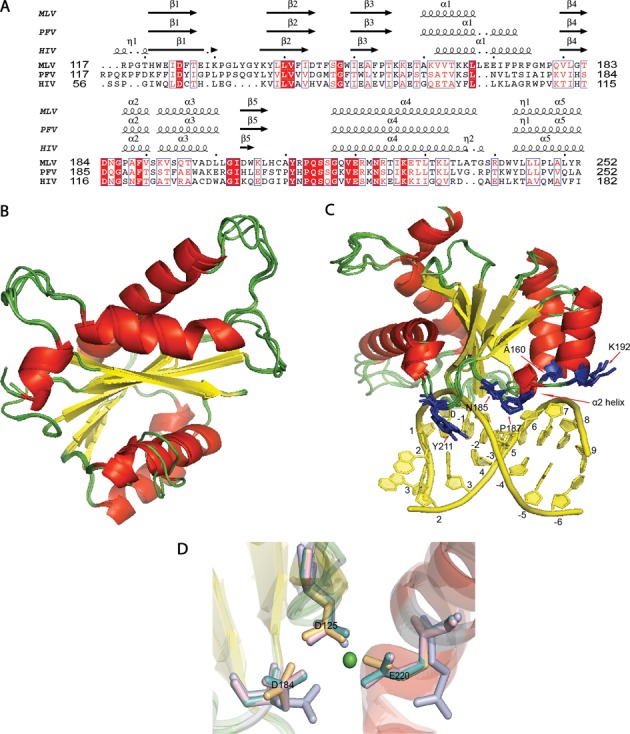
MLV IN CCD. (A) Structure-based sequence alignment of PFV and MLV CCD shows the homologous tDNA binding residues of PFV in MLV. Residues 117–252 for MLV CCD IN, 117–252 for PFV CCD IN and 56–182 for HIV CCD IN are displayed. T163 in PFV corresponds to A160 in MLV, Q186 in PFV corresponds to N185 in MLV, A188 in PFV corresponds to P187 in MLV, S193 in PFV corresponds to K192 in MLV and Y212 in PFV corresponds to Y211 in MLV. PROMALS3D structure-based sequence alignment is displayed using the ESPRIPT server (35). (B) Residues 117–271 of MLV CCD IN were modeled using three different servers as mentioned in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. An overlay of the three MLV CCD INs with PFV CCD IN (PDB ID: 3OS1) is presented. The alpha helices are represented in red, the beta sheets are represented in yellow and the loops are represented in green. (C) PFV CCD along with the three homology models of MLV CCD is displayed. The tDNA double helix is represented in yellow and was obtained from the PDB ID: 3OS1. tDNA binding residues (blue side chain) of PFV CCD overlaid with the MLV CCD residues predicted to bind tDNA. There is overall agreement in the orientation of the tDNA residue side chains among all the models. The five homologous tDNA binding residues in MLV CCD are A160, N185, P187, K192 and Y211. (D) View of the active site of IN is shown in this figure. The secondary structural elements are colored according to the scheme as in (A). The side chain of the active site residues of PFV CCD (light teal), SWISS-MODEL MLV CCD (light magenta), ITASSER MLV CCD (light blue) and MMM-tree MLV CCD (light orange) is aligned to show the conservation of their architecture. The catalytic triad of D125, D184 and E221 of each of the structures are shown aligned in the presence of a single Mg+2 ion (green sphere) of the PFV IN structure (PDB ID: 3OS1).
