Figure 2.
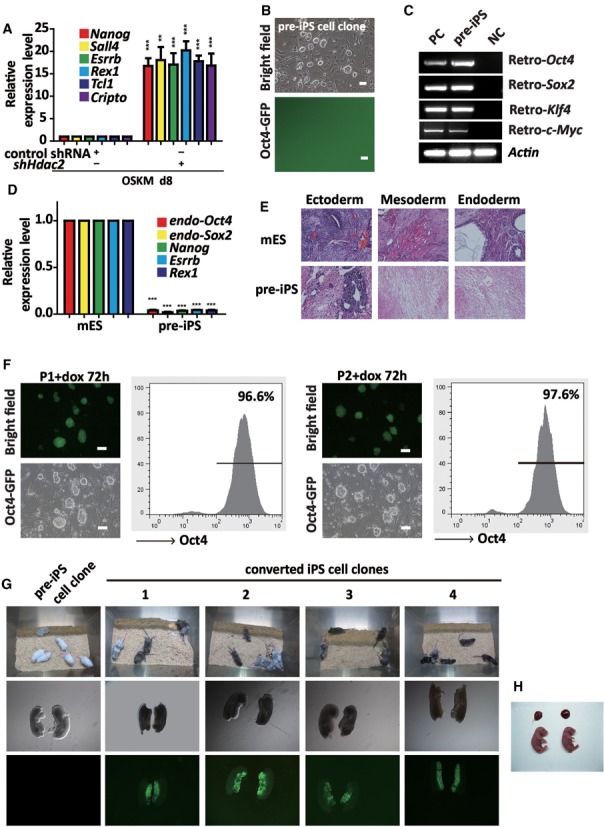
Knockdown of Hdac2 promotes the further reprogramming of pre-iPS cells. (A) qRT-PCR analyses of maturation phase-related genes in MEFs under reprogramming (day 8) infected with OSKM in combination with control shRNA or shHdac2. (B) Phase contrast (upper panel) and fluorescence (lower panel) microscopic images showing the morphology of a typical mES-like but GFP-negative pre-iPS cell clone. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) RT-PCR was performed to confirm Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc transgene expression in the pre-iPS cells. OG-MEFs were used as a negative control (NC) and OG-MEFs infected with the OSKM viruses were used as positive controls (PC). (D) qRT-PCR analyses of the pluripotency genes in the pre-iPS cells. The mRNA levels are shown relative to the mES cells. Actin was used as an internal control. (E) HE staining of teratomas derived from mES cells and pre-iPS cells. (F) Morphology of P1 and P2 clones by dox-inducible Hdac2 knockdown after treatment with dox for 72 h. A FACS analysis showed the proportion of Oct4-GFP cells after dox treatment. Scale bar, 100 μm. (G) Two-week-old chimeric mice derived from P1 and four converted iPS cell clones (1, 2, 3 and 4; C57BL/6 background). (H) Two live-born (E18.5) all-iPS cell mice generated from C4-iPS cells via tetraploid complementation assay (TCA). The data in a and d represent the means ± S. E. M. of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student's t-test).
