Figure 4.
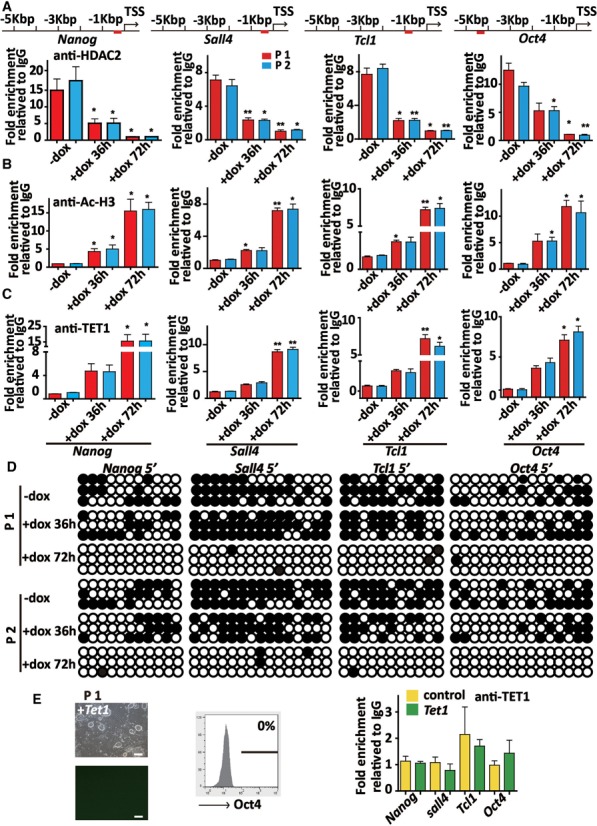
Histone acetylation is primarily required for DNA demethylation and maturation phase-related gene activation in the maturation of iPS cells. (A) ChIP-qPCR analysis of HDAC2 binding to the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 and P2 clones before and after dox treatment for 36 and 72 h. The fold enrichment relative to IgG controls is shown. (B) ChIP-qPCR analysis of the level of Ac-H3 binding to the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 and P2 clones before and after dox treatment at 36 and 72 h. (C) ChIP-qPCR assay showing the binding of TET1 to the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 and P2 clones before and after dox treatment for 36 and 72 h. (D) Bisulfite sequencing of the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 and P2 clones before and after dox treatment for 36 and 72 h. (E) Phase and Oct4-GFP images of P1 clone transfected with Tet1 (left). Scale bar, 100 μm. Flow cytometry analysis of Oct4-GFP reporter activity (middle). ChIP-qPCR analysis of the binding of TET1 to the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 clone transfected with or without Tet1 (right). The data in A, B, C and E represent the means ± S. E. M. of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student's t-test).
