Figure 5.
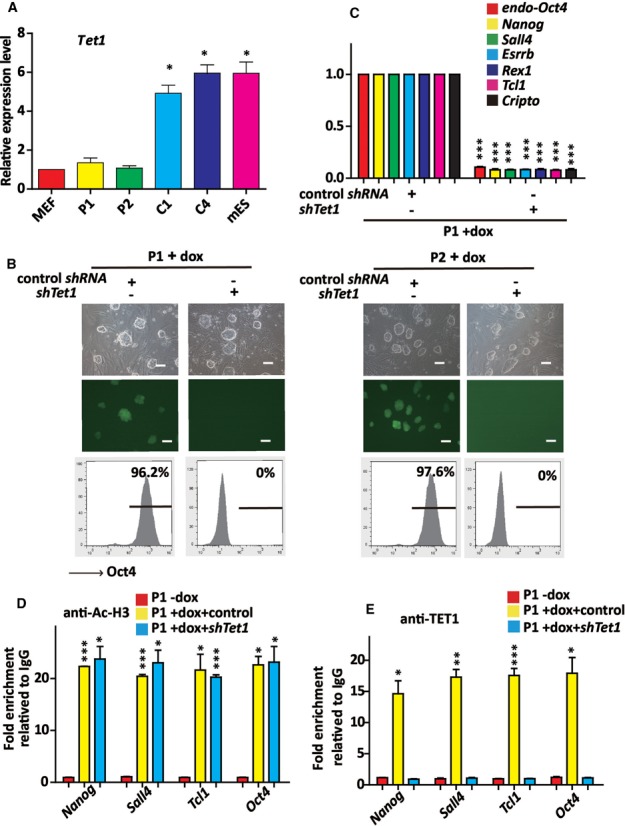
TET1-mediated DNA demethylation is critically involved in Hdac2 knockdown-induced iPS cell maturation. (A) qTR-PCR analysis of Tet1 expression in MEFs, P1, P2, C1, C4 and mES cells. Actin was used as an internal control. (B) Phase and Oct4-GFP images of P1 and P2 clones transfected with control shRNA and shTet1 under dox treatment (upper). Scale bar, 100 μm. Flow cytometry analysis of the proportion of Oct4-GFP cells in P1 and P2 clones transfected with control shRNA and shTet1 under dox treatment (below). (C) qRT-PCR analysis of maturation phase genes in P1 clone transfected with control shRNA and shTet1 upon dox treatment. The mRNA levels normalized to Actin are relatived to that of the control (the P1 clone transfected with control shRNA under dox treatment). (D) The ChIP-qPCR assay showed the level of Ac-H3 to the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 clone transfected with control shRNA, shTet1 under dox treatment for 72 h. The fold enrichment relative to IgG controls is shown. (E) The ChIP-qPCR assay showed the binding of TET1 to the Nanog, Sall4, Tcl1 and Oct4 promoters in P1 clone transfected with control shRNA, shTet1 under dox treatment for 72 h. The fold enrichment relative to IgG controls is shown. The data in A, C, D and E represent the means ± S. E. M. of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student's t-test).
