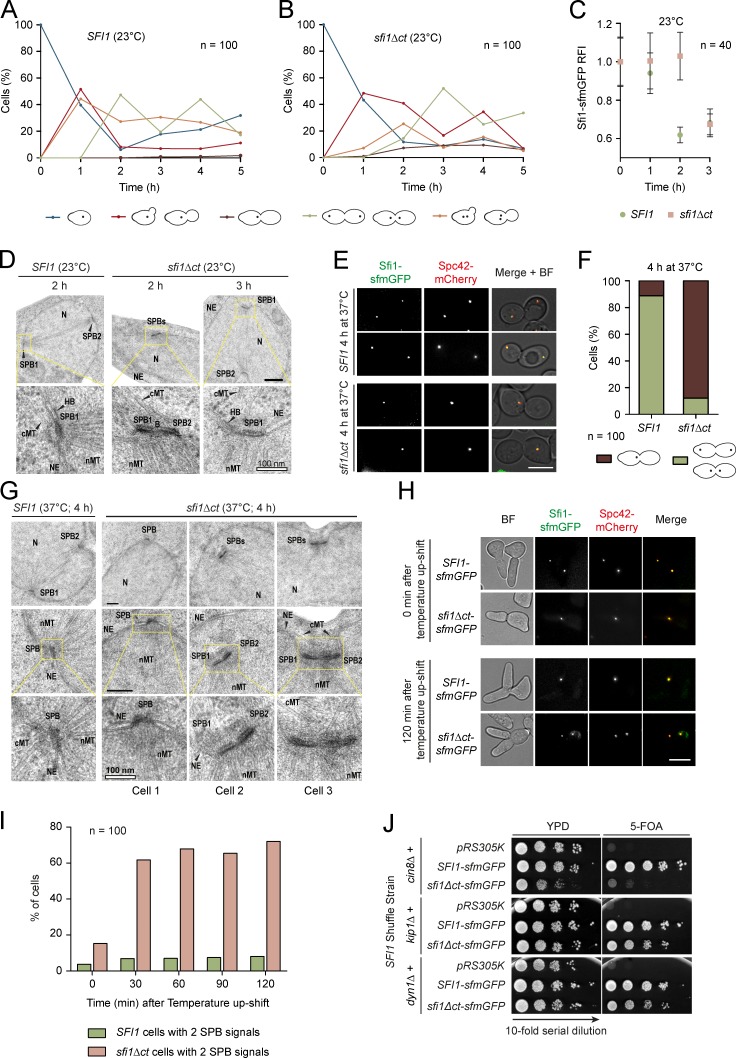
Figure 7.
Sfi1 C terminus is important for bridge integrity. (A and B) The effect of sfi1Δct on cellular fitness at 23°C. The Sfi1-sfmGFP signal was followed in α-factor–synchronized cells. The different cell morphologies observed are indicated. (C) Quantification of the Sfi1-sfmGFP signal of the major morphologies observed at time points 0–3 h in A and B. (D) SPB morphology of sfi1Δct cells at 23°C. Representative EM pictures are shown. 10 cells were analyzed per time point. NE, nuclear envelope; cMT, cytoplasmic microtubules; nMT, nuclear microtubules; N, nucleus; B, bridge. (E) The effect of sfi1Δct on SPB duplication at 37°C. Synchronized cells were shifted to 37°C upon α-factor washout and cell fate was followed over 4 h. Two representative large-budded cells of the indicated strains are shown. (F) Quantification of metaphase cells from E. (G) SPB morphology of SFI1 and sfi1Δct cells from E. In D and G, panels boxed in yellow are enlarged below. (H) Importance of Sfi1-CT for bridge stability. SFI1 and sfi1Δct cells were arrested in G1/S by SIC1 overexpression at 23°C. Cells were shifted to 37°C and the SPB signal was monitored over time. (I) Quantification of H. (J) Synthetic lethality test between sfi1Δct and cin8Δ, kip1Δ, and dyn1Δ. Serial dilutions of cells were tested for growth at 23°C. n, number of cells analyzed per time point. Bars: (D and G) 200 nm, where not otherwise indicated; (E and H) 5 µm.