Figure 1.
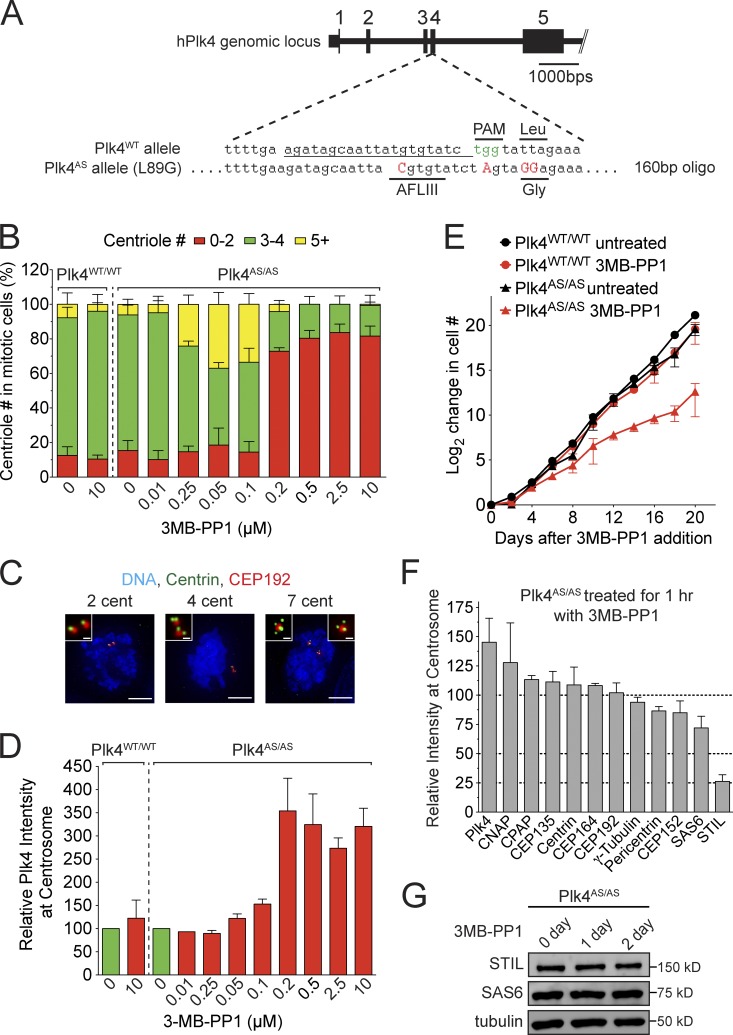
Plk4 kinase activity is required to maintain STIL at the centriole. (A) Schematic of the strategy used to knock-in the AS mutation into both alleles of Plk4 in human DLD-1 cells. The repair oligonucleotide introduced the AS mutation (L89G), a silent AflIII restriction site, and a mutation in the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) to prevent recutting by SpCas9 after homology-directed repair. (B) Plk4WT/WT or Plk4AS/AS cells were treated with 3MB-PP1 for 20 h and nocodazole was added for the final 4 h of the treatment. The graph shows the fraction of mitotic cells with the indicated number of centrioles. Bars represent the mean of three independent experiments, with >20 cells counted per experiment. (C) Selected images of mitotic Plk4AS/AS cells from B stained with Centrin and CEP192. Bars: (large images) 5 µm; (inset images) 0.5 µm. (D) Quantification of the relative levels of Plk4 at the centrosome of interphase cells 20 h after addition of 3MB-PP1. Bars represent the mean of at least three independent experiments, with >40 cells counted per experiment. (E) Graph showing the increase in cell number at various times after addition of 3MB-PP1. Points show the mean of at least three independent experiments. (F) Quantification of relative protein abundance at the centrosome of S/G2 phase cells 1 h after the addition of 3MB-PP1. Bars represent the mean of three independent experiments, with >40 cells counted per experiment. (G) Immunoblot showing no change in the level of endogenous STIL and SAS6 at 1 or 2 d after Plk4 inhibition with 3MB-PP1. All error bars represent the SEM.