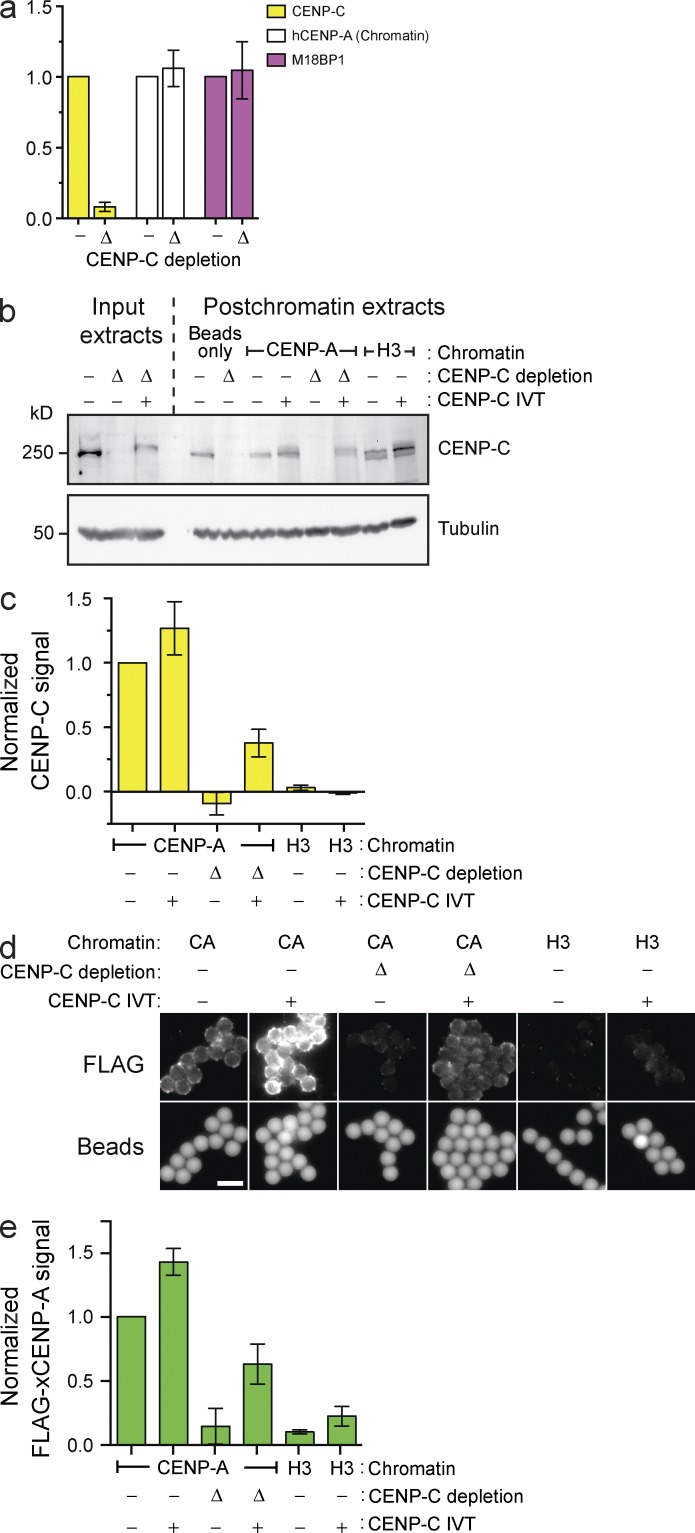
Figure 2.
CENP-C depletion prevents in vitro CENP-A assembly but not M18BP1 recruitment. (a) Levels of CENP-C, hCENP-A, and M18BP1 on chromatin beads after bead incubation in mock-depleted (−) or CENP-C–depleted (Δ) extracts. All bar graphs represent means ± SEM; n = 4. (b) The levels of CENP-C protein in egg extracts before (Input extracts) or after (Postchromatin extracts) incubation of chromatin beads in the extract and CENP-A assembly. The extracts were mock depleted (−), CENP-C depleted (Δ), or complemented with CENP-C (+). Tubulin is shown as a loading control. (c) CENP-C signal on chromatin was assessed after the experiment described in b; n = 3. (d) Representative images showing FLAG–xCENP-A assembly on chromatin beads as described in b. The FLAG–xCENP-A signal (top row) and the bead autofluorescence (bottom row) are shown. Bar, 5 µm. (e) Quantification of FLAG–xCENP-A assembly assays described in d; n = 3.