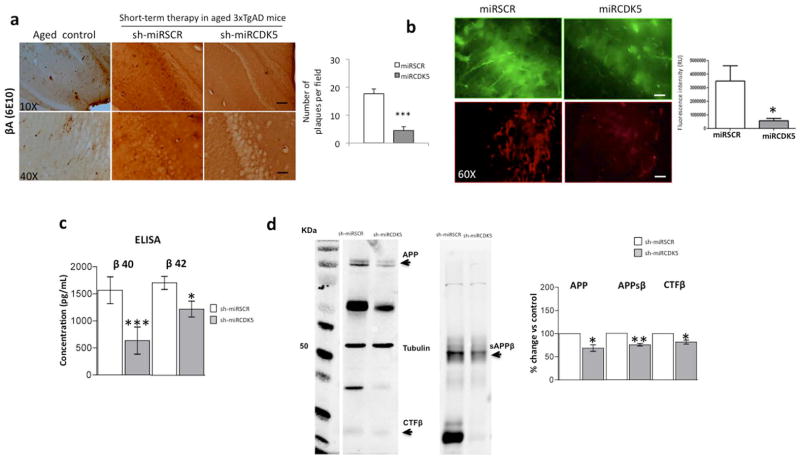
Figure 1.
shCDK5miR treatment reduced amyloid deposition in the hippocampus at 3 weeks after administration. a) βA immunohistochemistry revealed a reduction in extracellular β-amyloid plaques in animals injected (short-term) with shCDK5miR compared to scrambled (shSCRmiR) injection in 18-month-old 3xTgAD mouse hippocampi and aged control mice. Magnification, 10X and 40X, scale bar, 100 μm and 20 μm. n=3–4. b) The fluorescence intensity of intracellular βA was diminished by short-term therapy with shCDK5miR in the hippocampal CA1 area of 3xTg-AD mice. Representative images of green fluorescence from pAAV.CMV.hrGFP for the shSCRmiR and shCDK5miR conditions are shown. c) These results were confirmed by a decrease in βA 1-40 and βA 1-42 levels measured using ELISA in the hippocampus of 18-month-old 3xTgAD mice injected with shCDK5miR or shSCRmiR. d) Western blots of APP, sAPPβ and CTFβ revealed a reduction in protein levels 3 weeks after the injection of shCDK5miR in 18-month-old 3xTgAD mice. Tubulin was used as a loading control, and densitometry quantification was performed. n= 5, *=p<0.05, **=p<0.01, ***=p<0.001.