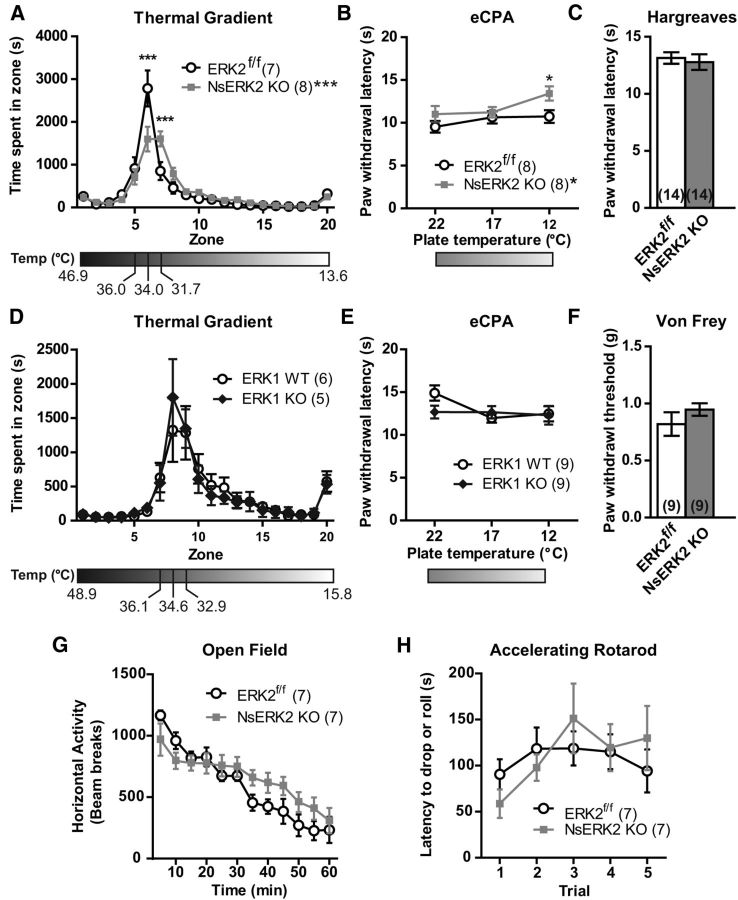
Figure 2.
Conditional deletion of ERK2 impairs cold sensation without affecting heat or mechanical thresholds. A, D, NsERK2 KO (A; n = 7 or 8/group) and ERK1 KO (D; n = 5 or 6/group) mice were assessed for thermotaxis behavior during a 2 h trial on temperature gradient ranging from 49°C to 13°C. Anymaze software (Stoelting) was used to measure time that the mouse's center of mass spent in each zone during the entire test (mean ± SEM). ***p < 0.001. B, E, Using the extended cold plantar assay, paw withdrawal latency (seconds) to a cold stimulus in NsERK2 KO (B; n = 8/group) and ERK1 KO (E; n = 9/group) mice was measured and compared with control littermates on glass held at room temperature (22°C) or cooled to either 17°C or 12°C. *p < 0.05. C, NsERK2 KO (n = 14) and ERK2f/f (n = 14) control littermates were assessed for paw withdrawal latency (seconds) to a radiant heat source using the Hargreaves test. F, NsERK2 KO (n = 9) and ERK2f/f (n = 9) control littermates were assessed for paw withdrawal thresholds (in grams) using calibrated von Frey filaments. Data for paw withdrawal latencies and thresholds are expressed as mean ± SEM. G, Open field locomotor behavior was assessed over 1 h in NsERK2 KO (n = 7) and ERK2f/f (n = 7) control littermates. Data are binned into 5 min intervals and expressed as mean ± SEM. H, Time to fall off of an accelerating Rotarod was measured in both NsERK2 KO (n = 7) and ERK2f/f (n = 7) control littermates. Data are graphed for each of the five trials and expressed as mean ± SEM.