FIGURE 1.
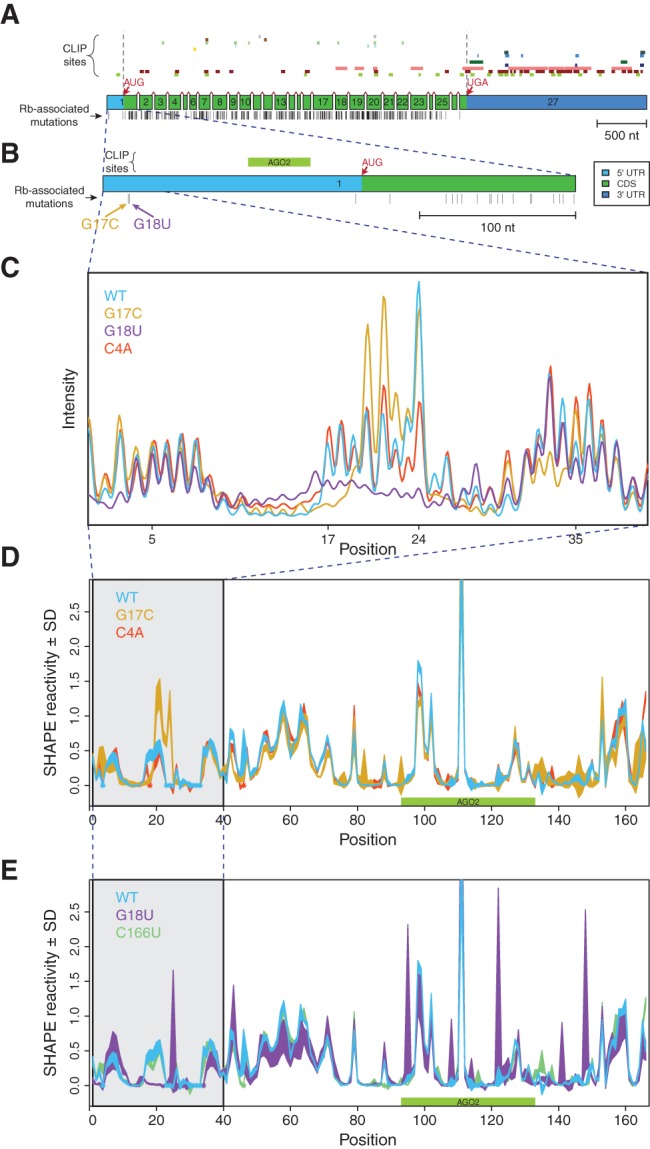
Disease-associated mutations in the 5′ UTR of RB1 change its SHAPE profile. (A) RB1 gene structure, protein-binding sites, and locations of retinoblastoma-associated mutations with reference to the 27 exons of the gene. (Top) Experimentally determined PAR-CLIP (Photoactivatable-Ribonucleoside-Enhanced Crosslinking and Immunoprecipitation) RNA binding protein (RBP) sites obtained from doRiNA database, from top to bottom: R521H, FUS, EWSR1, FMR1 isoform 1, FMR1 isoform 7, C17ORF85, PUM2, TIAL1, FXR2, ZC3H7B, TIA1, IGF2BP1-3, AGO1-4, ELAV1 (Anders et al. 2012). We observed that a majority of RBP binding sites are in the 3′ UTR and coding sequence. (Middle) Exons of the RB1 gene, to scale, including splice junctions. Light blue: 5′ UTR, green: coding sequence (CDS), dark blue: 3′ UTR. (Bottom) Positions of known retinoblastoma-associated point mutations, insertions, and deletions, from the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD), indicated as vertical black bars (Stenson et al. 2003; George et al. 2008). (B) Close-up schematic of exon 1 with a single PAR-CLIP site (Argonaute 2) mapping to the 5′ UTR. Corresponding retinoblastoma-associated mutations, G17C and G18U, which were previously predicted to alter the UTR structure (Halvorsen et al. 2010). (C) Representative raw SHAPE (selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension) capillary electrophoresis traces for the WT (blue), G17C (gold), G18U (purple), and C4A (red) UTRs before normalization and averaging. Differences between the sequences across positions 17–24 show that the two disease-associated mutations result in large structural changes as predicted. (D,E) Normalized SHAPE profiles for wild-type, mutant, and structural control UTRs; area represents mean ± SD normalized SHAPE values over five repeats. The region containing nucleotides with mutation-induced structure change are highlighted in gray. Asterisks (in color) indicate positions where the background control peak was too high to accurately determine SHAPE reactivity for the nucleotide. (D) WT (blue), G17C (gold), C4A (structural control; red). (E) WT (blue), G18U (purple), C166U (structural control; green).
