FIGURE 4.
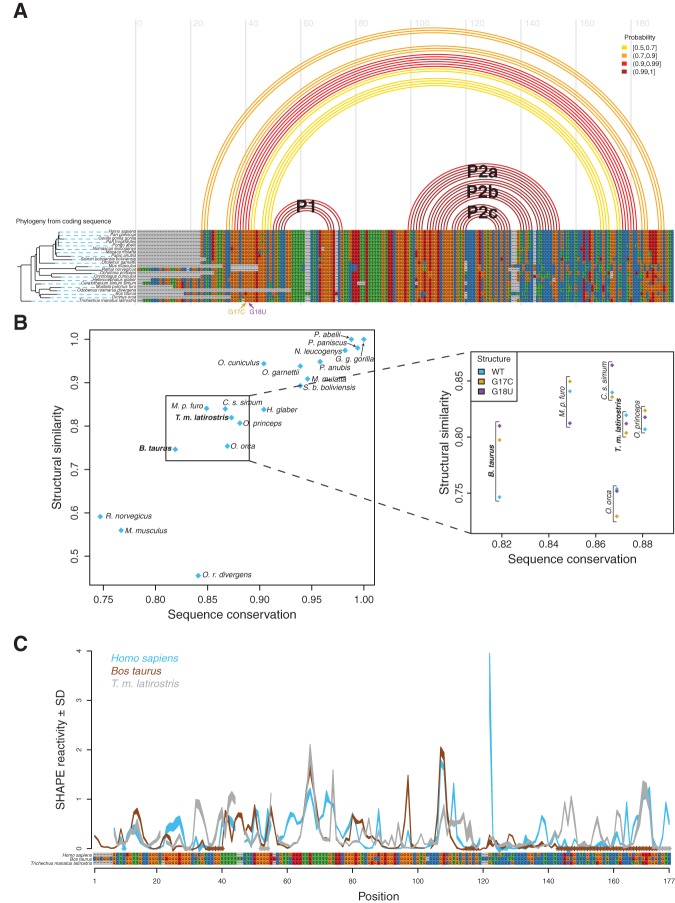
Comparative sequence analysis predicts manatee and domestic cow RB1 5′ UTRs have conserved structural features present in the human construct. (A) (Top) Ensemble of human structures for the RB1 WT 5′ UTR, represented by predicted arcs colored by base-pairing probability. (Bottom) Multiple sequence alignment of the RB1 5′ UTR, showing that the UTR is highly conserved in mammals. Phylogenetic tree was created from the RB1 protein sequence from each organism (Supplemental Fig. S3). The length of the black branches indicates evolutionary distance, and the dashed blue lines connect the leaves of the tree to their corresponding organism. (B) (x-axis) Sequence similarity score. (y-axis) Structural similarity score (consistency of each sequence from the alignment to the SHAPE-directed partition function for human WT). The sequences we are interested in, which are most divergent in sequence yet highly conserved in structure, are easily visualized by trending to the top left corner. We used this plot to identify candidate UTR sequences for further SHAPE structural characterization. We chose to study the domestic cow (B. taurus) as it diverges significantly from human in sequence but has a relatively high structural similarity. In addition, the transcription start site of the cow RB1 5′ UTR was recently verified experimentally (Zimin et al. 2009, 2012). The manatee RB1 5′ UTR was chosen for further experimental characterization since it is structurally similar to human WT (blue diamond, inset) and differs significantly from G17C and G18U (gold and purple diamonds, inset). (C) SHAPE structure probing for human (blue), domestic cow (brown), and manatee (gray) mapped onto the alignment of these sequences. Qualitative similarities in the protection patterns suggest similar properties of the RNA structural ensemble.