FIGURE 4.
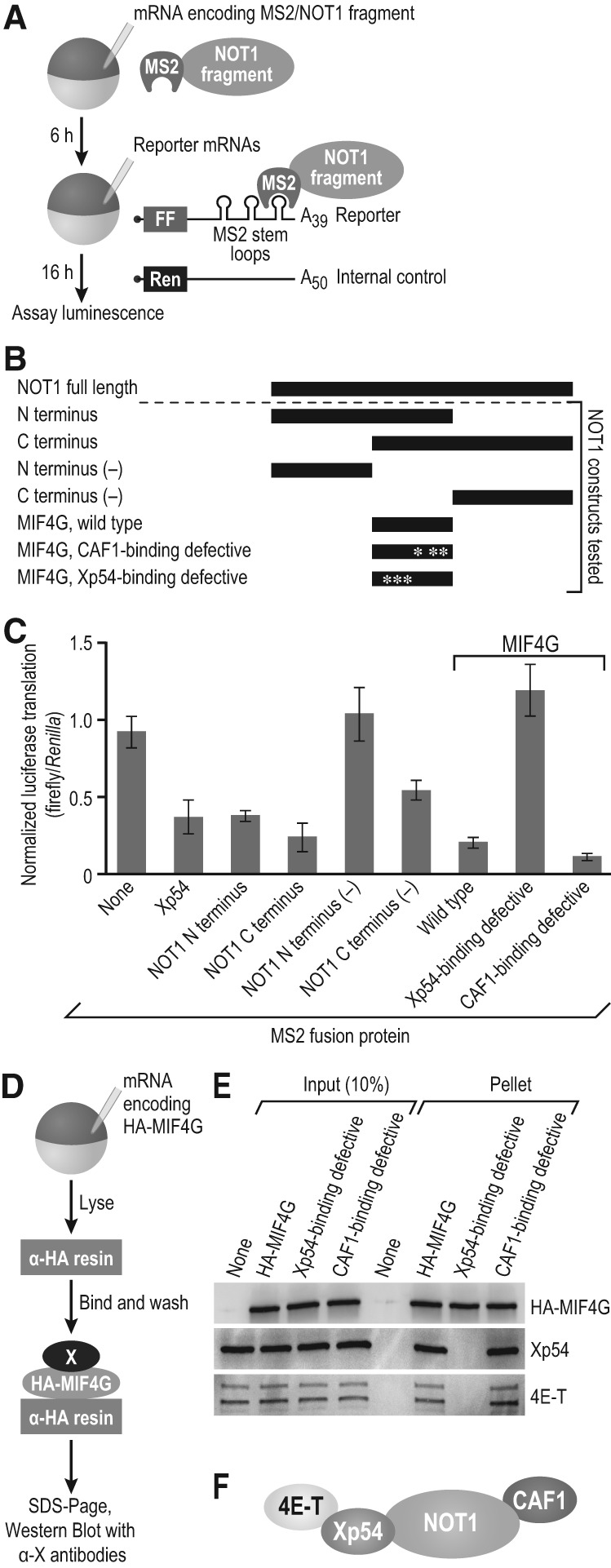
NOT1 MIF4G-Xp54 interaction is required for repression. (A) Schematic of tethered function assay with NOT1 fragments. (FF) firefly luciferase, (Ren) Renilla luciferase. (B) NOT1 fragments used in the tethered function assay. Mutations were made in the NOT1 MIF4G domain to obtain Xp54- and CAF1-binding defective constructs, as indicated by asterisks. Full-length NOT1 is depicted for scale. (C) Results of tethered function assay, normalized to “no MS2 protein” control (none). Xp54 was used as a control for repression. Three independent experiments were performed, with four oocyte replicates each time. Error bars represent 1 SD. Student's two-tailed t-test was used to compare the NOT1 amino terminus to amino terminus (−) and the wild-type MIF4G to the Xp54-binding defective MIF4G. Both were significantly (P < 0.005) different. (D) Schematic of the coimmunoprecipitation assay with HA-MIF4G (the NOT1 MIF4G domain) as the bait protein. HA-MIF4G WT, the CAF1-binding deficient mutant of the MIF4G domain, and the Xp54-binding deficient mutant were used. (E) Western blots were conducted to test whether 4E-T and Xp54 interact with the Xp54-binding deficient MIF4G domain. Western blots depict a single representative experiment, and three biological replicates were conducted. (F) Model of the interactions between NOT1, CAF1, Xp54, and 4E-T.
