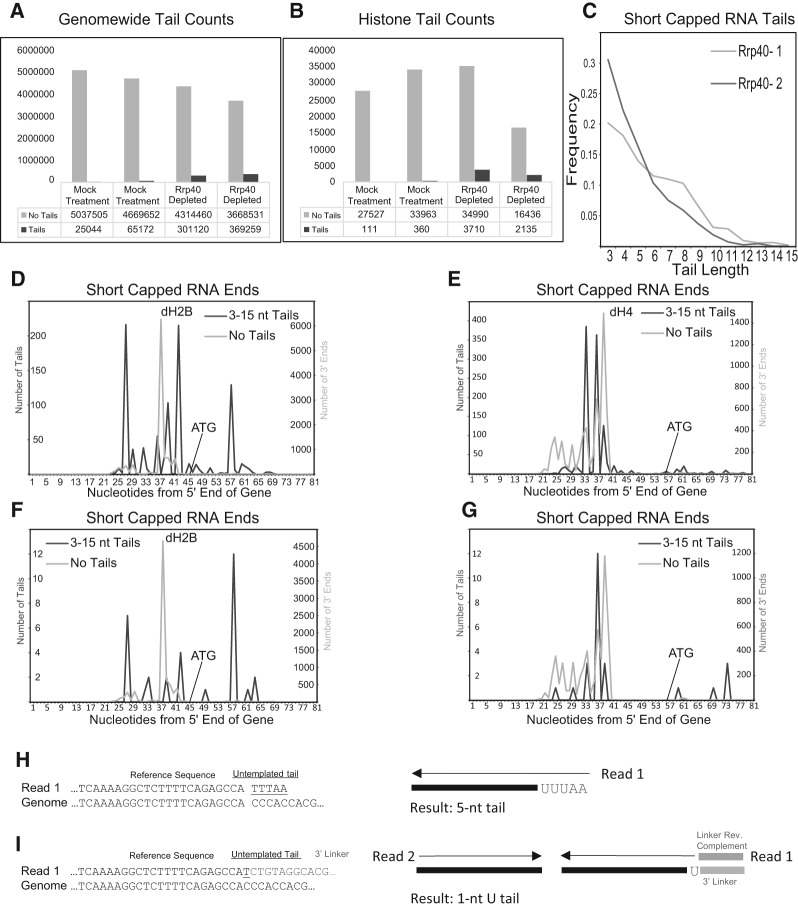
FIGURE 5.
AppEnD analysis of nontemplated tails on short capped transcripts. (A) We obtained the sequence data for paused capped RNAs from Drosophila tissue culture cells with and without exosome knockdown from Adelman and coworkers (Henriques et al. 2013), and analyzed the data using AppEnD. Note that the experimental results were generated by an approach different from EnD-Seq. These RNAs were sequenced from the 3′ end after ligation of the Illumina primer to the RNA, making it possible to reliably detect only tails 3 nt or longer. The number of reads that mapped with no tails (light gray) or tails (dark gray) are shown with or without knockdown of the exosome subunit Rrp40. (B) We obtained the reads on the tandemly repeated histone genes (not mapped in the initial paper) from the same data set by mapping the data to a Drosophila genome in which we placed a single histone repeat. (C) The length distribution of the tails 3 nt or longer, which were essentially all oligo(A) tails with occasional substitutions of a C or U in the A tail, is shown. (D,E) The distribution of sequences ending at the indicated nucleotide in the histone H2B (D) and histone H4 gene is shown in the sample with rrp40 knocked down. The light gray line is the untailed RNAs, and the dark gray line is the tailed RNAs. (F,G) Same as (D) and (E) but for the control sample (expressing Rrp40). Note that the patterns of tail additions match (D) and (E) well but there are far fewer tail additions. (H) Example of how AppEnD identifies and maps a short capped RNA read with a nontemplated tail. Very short tails (shorter than 3 nt) cannot be reliably be identified in this case because there is no 3′ linker marking the precise end of transcription. (I) Example showing how EnD-Seq with AppEnD can detect nontemplated additions as short as 1 nt due to the presence of the 3′ linker sequence in the read.