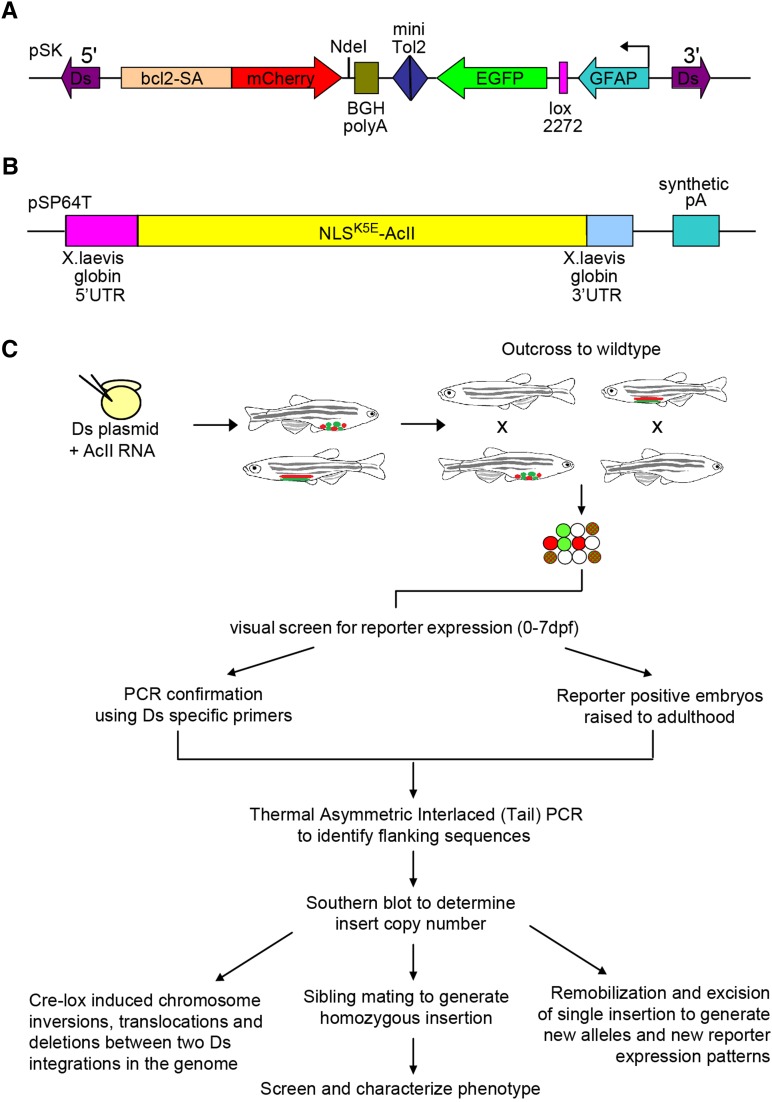
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the multi-functional Ac/Ds transposon system and insertion screen. (A) The pDsDELGT4 vector consists of a protein trap unit and an enhancer trap unit. The protein trap unit is close to the Ds 5′ terminal repeat sequences. The mCherry coding sequence without the first methionine (red) is flanked by the zebrafish B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 (bcl2) splice acceptor sequence and the bovine growth hormone (BGH) polyadenylation signal. In the reverse orientation, close to the Ds 3′ terminal repeat sequences, the enhancer trap reporter GFP (green) is downstream of a short glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoter and a lox2272 site. A mini Tol2 sequence is present between the two trap units (blue). (B) Schematic representation of the construct for synthesizing Ac transposase mRNA, with 5′UTR and 3′UTR sequences from the Xenopus globin gene. (C) Overview of the DsDELGT4 mutagenesis screen. pDsDELGT4 plasmid was co-injected with capped Ac mRNA into one-cell stage embryos (F0). Founders with transient reporter expression were raised to adulthood and mated with wild-type (AB) fish. F1 embryos were visually screened for reporter expression from fertilization until 7 d after fertilization. Ds integrations were verified by PCR using Ds specific primers. Reporter positive F1 embryos were raised to adulthood. TAIL-PCR and Southern hybridization were performed with genomic DNA isolated from the tail-fin of F1 fish and subsequent generations to map the integrations and determine the number of Ds insertions. Phenotype analysis of homozygous mutants generated by mating siblings with the same integration was performed. Cre-mediated recombination between two Ds integrations was performed to generate precise segmental deletions.