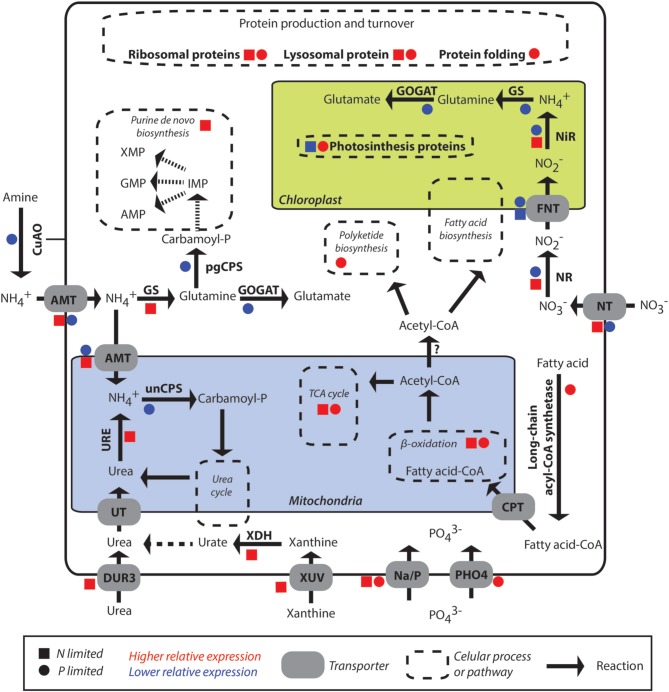
Figure 2.
Overview of differentially expressed pathways and genes of P. parvum grown to N- or P-limitation, relative to nutrient replete cultures. Squares indicate response under N-limitation compared to the replete condition, while circles indicate response under P-limitation compared to the replete condition. Red and blue indicate up- and down-regulation respectively. AMT, ammonium transporter; CPT, carnithine palmitoyl transferase; CuAO, Copper amine oxidase; DUR3 and UT, urea transporter; FNT, formate/nitrite transporter; GOGAT, glutamate synthase; GS, glutamine synthetase; Na/P, sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate transporter; NiR, nitrite reductase; NR, nitrate reductase; NT, nitrate transporter; pgCPS, carbamoyl phosphate synthase (involved in pyrimidine syntheses, uses glutamine as substrate); PHO4, phosphate transporter of the pho4 family; unCPS, carbamoyl phosphate synthase (involved in the urea cycle, uses ammonium as substrate); URE, urease; XDH, xanthine dehydrogenase; XUV, xanthine-uracil permease.