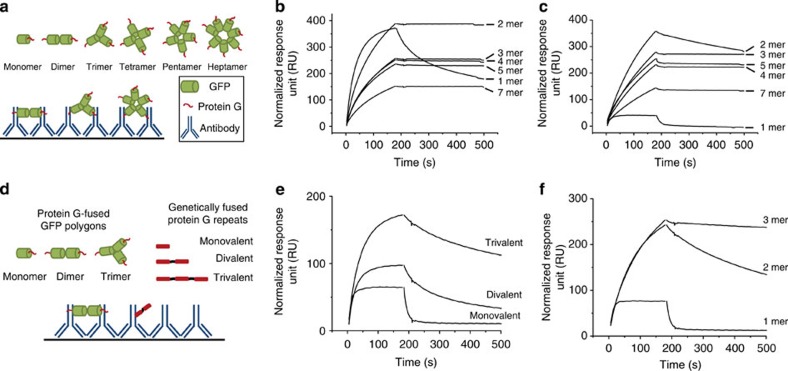
Figure 5. Multivalent interactions of protein G-functionalized GFP polygons.
(a) Schematic representation of the multivalent interactions between surface-bound antibodies and protein G polygons. Multivalent protein G polygons (dimer to heptamer) and monomeric protein G-GFP were applied on the surface-bound antibodies. (b,c) SPR responses on the associations (180 s) and dissociations (320 s) of multivalent protein G polygons against human (b) or mouse (c) antibodies. Constant mass concentrations of protein G polygons (5 μg ml−1 for human and 10 μg ml−1 for mouse antibodies) were used to maintain constant concentrations of the protein G unit, regardless of the valency. (d) Schematic representation of the interactions of surface-bound antibodies with protein G polygons (mono-, di- and trimers) or with genetically fused protein G (mono-,di- and trivalent) repeats. (e,f) SPR responses on the associations (180 s) and dissociations (320 s) of genetically fused protein G repeats (e) or protein G polygons (f) against mouse antibodies. All binding curves were normalized by subtracting the reflective index changes on sample injections.