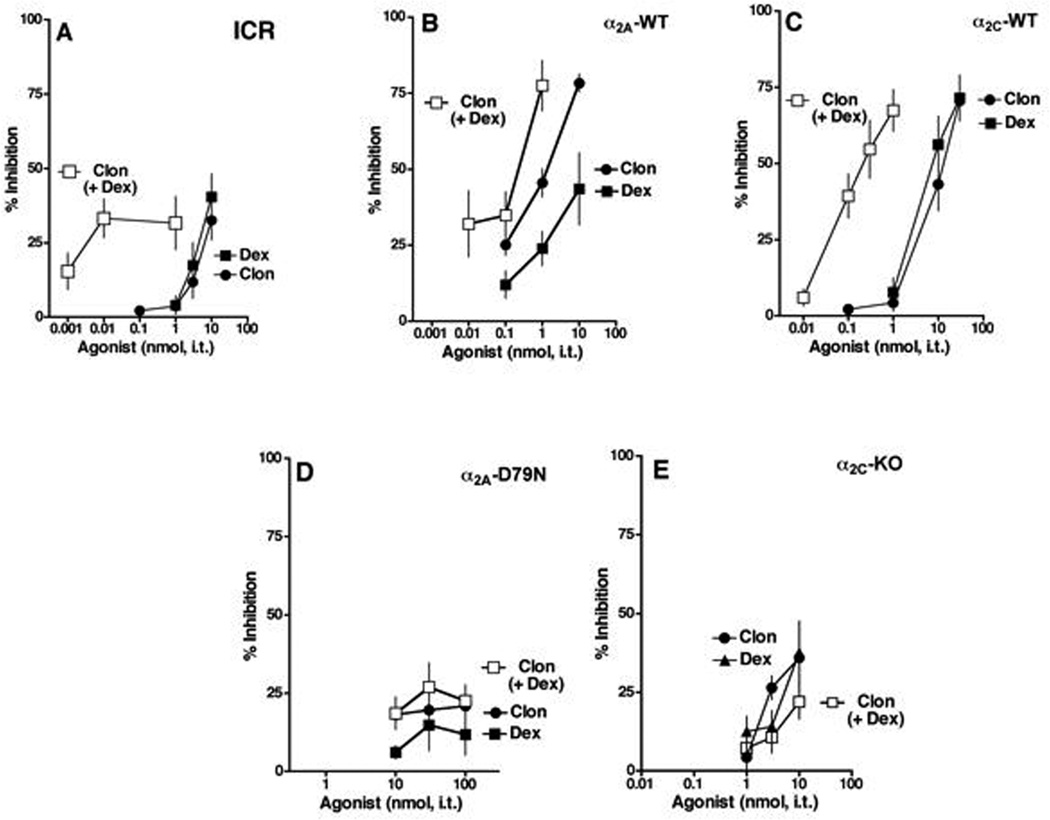
Figure 5. Clonidine- and dexmedetomidine-induced sedation/motor impairment.
A–E. Rotarod performance was challenged by intrathecally administered clonidine, dexmedetomidine or both in ICR (A), α2AAR-WT (B), α2CAR-WT (C), α2AAR-D79N (D) and α2CAR-KO mice (E). Neither clonidine (●), dexmedetomidine (■) nor the 1:1 combination (□) exhibited greater than 40% efficacy up to the highest doses used in the SP test. The combination did, however, result in the production of this modest efficacy at lower doses, representing significant potentiation. B. In α2AAR-WT mice, clonidine exhibited full efficacy at 10 nmol (●) whereas dexmedetomidine's maximum efficacy at that dose fell short of 50% (■). The 1:1 combination (□) dose-response curve shifted significantly to the left (~10-fold) relative to clonidine alone with comparable efficacy and the interaction was found to be synergistic (isobologram not shown; p<0.05; t-test). C. In α2CAR-WT mice both clonidine and dexmedetomidine inhibited rotarod performance with full efficacy. The 1:1 combination (□) dose-response curve shifted significantly to the left (~100-fold) relative to either drug alone with comparable efficacy and the interaction was found to be synergistic (isobologram not shown; p<0.05; t-test). D. In α2AAR-D79N mice, neither clonidine (●), dexmedetomidine (■) nor the 1:1 combination (◊) reduced rotarod performance more than 30%. E. α2CAR-KO mice, neither clonidine (●), dexmedetomidine (■) nor the 1:1 combination (□) reduced rotarod performance more than 50%. Group sizes were 5 mice/group. Abbreviations: CLON, clonidine; DEX, dexmedetomidine. ICR, Institute of Cancer Research; KO, knock-out; WT, wildtype.