Figure 1.
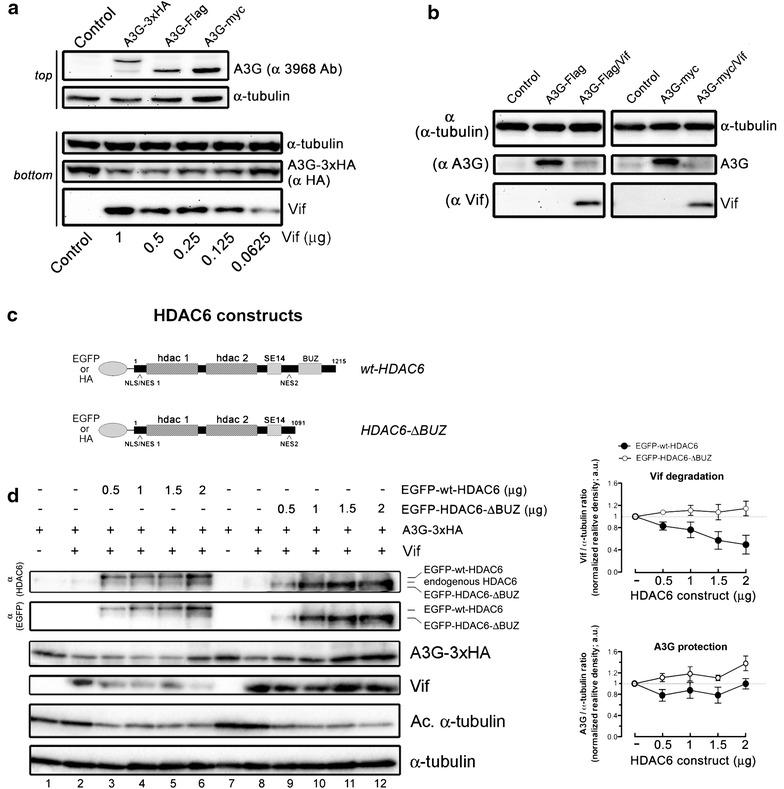
HDAC6 degrades Vif and protects A3G from Vif-mediated degradation. a, b Top-A, western blot analysis of different A3G-tagged proteins in cells lacking endogenous A3G expression (control). Bottom a, b, western blot analysis of Vif-mediated degradation of different A3G-tagged molecules. c Schematic representation of EGFP- or HA-tagged wt-HDAC6 and HDAC6-ΔBUZ constructs used in this study. The different domains are indicated: the nuclear localization signal (NLS) and export signal 1 and 2 (NES1/2), the two histone deacetylase domains (hdac 1 and 2) together with the SE14 region, and the BUZ domain (adapted from [56]). d Left, western blot of dose-response effects of EGFP-wt-HDAC6 and EGFP-HDAC6-ΔBUZ (detected by anti-HDAC6 or anti-EGFP abs, respectively) on Vif and A3G-3xHA. Lanes 1, 7 and 2, 8 are controls representing cells overexpressing only A3G-3xHA or A3G-3xHA together with Vif, respectively. Right, quantitation of western blots regarding EGFP-HDAC6- and EGFP-HDAC6-ΔBUZ-mediated Vif degradation (top) and A3G protection (bottom). In all western blots, α-tubulin is the control for total protein. When indicated, acetylated α-tubulin is a read-out for functional deacetylase activity of the different HDAC6 construct. All experiments were performed in HEK 293T cells. When indicated, endogenous HDAC6 expression level is shown. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of six independent experiments.
