Figure 6.
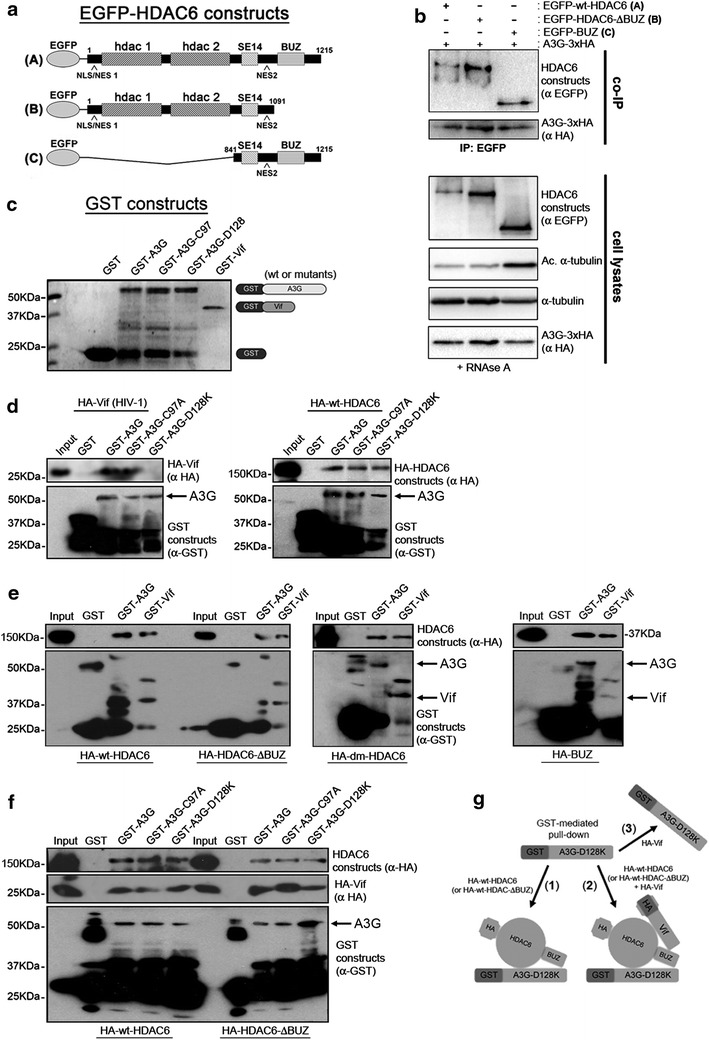
HDAC6 directly interacts with A3G and Vif to form a ternary complex. a Schematic representation of EGFP-HDAC6 constructs used in this assay. The constructs are (A) EGFP-wt-HDAC6, (B) a construct lacking the BUZ domain (EGFP-HDAC6-ΔBUZ) and (C) a construct bearing the BUZ domain. b RNAse A-treated cell lysates from HEK 293T cells co-expressing A3G-3xHA and each of the three EGFP-HDAC6 constructs [see (a)], were subjected to co-IP with anti-EGFP Ab, followed by immunoblotting with specific Abs against EGFP or HA. Input expression levels of each EGFP-HDAC6 construct used and overexpressed A3G-3xHA are shown in cell lysates-Western blots. α-tubulin was the control for total protein. Data shown are representative of three experiments. c–f Direct in vitro interaction of HDAC6 with A3G and Vif. Coomassie blue staining shows the electrophoretic migration profile of the recombinant GST, GST-A3G, GST-A3G mutants (C97A and D128K) and GST-Vif fusion proteins (c). Recombinant GST-proteins were incubated with purified in vitro translated HA-Vif [(d), left panel] or HA-HDAC6 proteins [(e); and (d), right panel] or both HA-Vif and HA-HDAC6 proteins (f). In f, a ternary GST-A3G-D128K/HA-HDAC6 construct-HA-Vif is shown. Bound Vif and HDAC6 proteins were fractionated on a 10% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody (upper panels). Anti-GST immunoblot shows the loading of the assayed GST-fusion proteins (lower panels). From b to f, a representative experiment of three is shown. g A scheme showing GST-mediated A3G-D128K established interactions, as follows: (1) with HDAC6 (wt or ΔBUZ constructs); and (2) with HDAC6 (wt or ΔBUZ constructs) in the presence of Vif to form a ternary A3G-D128K/HDAC6-Vif complex. In (3) it is represented the inability of Vif to interact with A3G-D128K.
