Fig 3. Gabapentin attenuates affective pain associated with traumatic nerve injury.
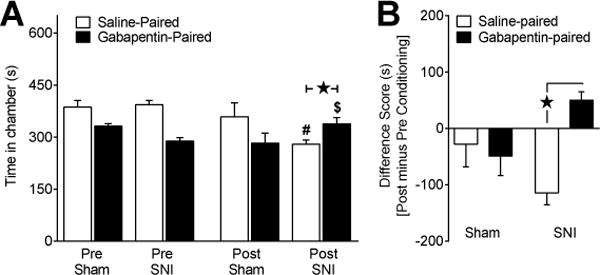
To determine affective pain relief we performed CPP with three days of conditioning (saline or gabapentin; 100 mg/kg; i.p.). (A) Time spent in the saline-paired chamber during preconditioning was greater than time spent in the gabapentin-paired chamber as a result of our biased drug-pairing approach. In sham rats (n=8), there was no change in preference during postconditioning (“Post”) when compared to preconditioning baselines (“Pre”). In SNI rats (n=17), gabapentin produced an increase in time spent in the gabapentin-paired chamber when compared to preconditioning baseline. (B) Saline and gabapentin difference scores were significantly different in SNI but not sham rats. These results taken together indicate gabapentin induces CPP thereby relieving affective pain in rats with traumatic nerve injury. # Significantly different from preconditioning saline-paired in SNI. $ Significantly different from preconditioning gabapentin-paired in SNI. ★ Significant difference between indicated groups.
