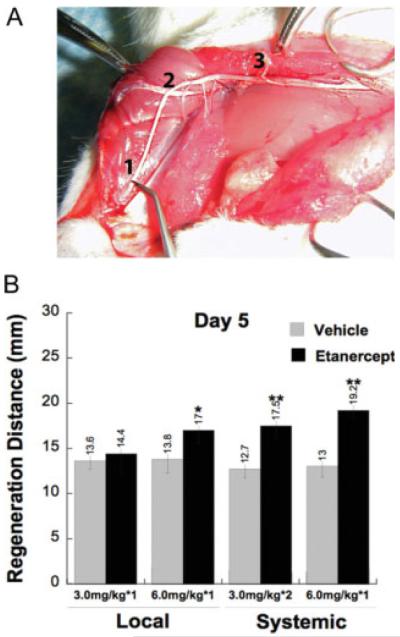
Fig. 2.
Etanercept therapy enhances functional regeneration of crushed sciatic nerve. A: An illustration of nerve pinch testing. Sciatic and tibial nerves are exposed in anesthetized rats, and 1-mm-long consecutive segments are pinched with a pair of forceps starting from the distal end of the tibial nerve (1), proceeding in the proximal direction until a reflex response is observed (2). The distance between this pinch site and the stitch marking the crush site (3) is measured under a dissecting microscope and defined as the regeneration distance in millimeters. B: Nerve pinch test measuring regeneration distance from the crush site (mm) at 5 days after immediate systemic, intraperitoneal (i.p.) or local epineurial administration of etanercept or vehicle after nerve crush injury. The regeneration rate was significantly enhanced after systemic and local administration of 6.0 mg/kg etanercept compared with vehicle. Single local administration of 3.0 mg/kg dose of etanercept was ineffective; however, when given twice i.p. at 1 hr and 3 days after crush, it significantly enhanced the regeneration rate compared with vehicle. Data are expressed as the mean 6 SEM regeneration distance of N = 5−6 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with vehicle-treated group by Mann-Whitney U-test.