Fig. 5.
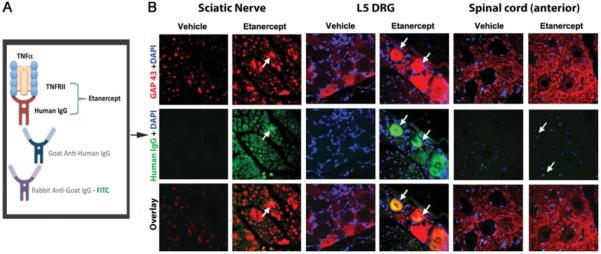
Colocalization of etanercept and GAP-43 in crushed nerve and associated DRG. A: Diagram for etanercept immunodetection method. Etanercept, a TNF-α-neutralizing agent that represents a fusion protein of TNFRII with the Fc portion of human IgG, is detected using goat anti-human IgG antibody and FITC-tagged rabbit anti-goat antibody. B: Dual immunofluorescence for GAP-43 (red) and etanercept (green) in the ipsilateral-to-injury proximal nerve segment, L5 DRG, and anterior horn of spinal cord after systemic administration of 6.0 mg/kg etanercept and vehicle treatments. Increased levels of GAP-43-positive fibers were observed in nerves, DRG, and spinal cord after etanercept therapy. In some GAP-43-immunoreactive nerve fibers, accumulation of etanercept was evident (arrows). Representative micrographs of N = 3 per group. ×400.
