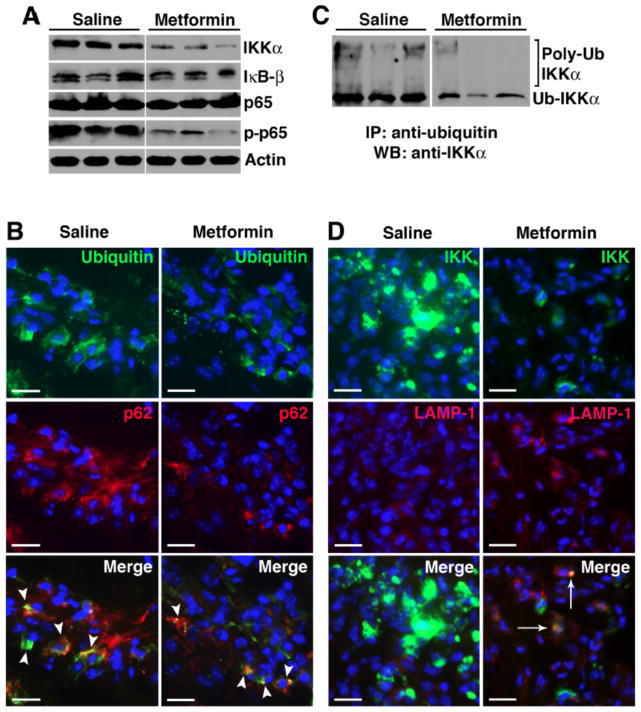
Figure 6. Metformin promotes selective degradation of NF-κB protein Iκ kinase (IKK) through autophagy.
(A) Day 9 paw lysates from saline controls and metformin-treated animals were probed for NF-κB proteins (IKKα, IκB-β, p65, and phospho-p65). Actin served as protein loading control. (B) Day 9 paw sections were probed for ubiquitin (green) and p62 (red). Colocalization (arrowheads, yellow) suggests ubiquinated-p62 aggregates. (C) Equivalent amounts of protein were immunoprecipitated with anti-ubiquitin antibody and probed with anti-IKKα antibody. High molecular weight protein complexes likely represent poly-ubiquinated IKKα. (D) Paw sections were also probed for IKKα and LAMP-1. Accumulation of IKKα was evident in the saline controls while IKKα level was significantly lower in metformin-treated animals. Colocalization of IKKα and LAMP-1 (arrows) in metformin treatment suggests IKKα targeted to the lysosomes.