FIGURE 3.
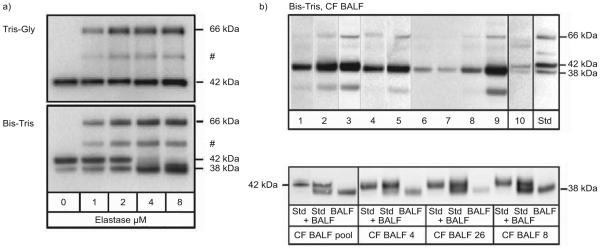
Molecular forms of SerpinB1 in cystic fibrosis (CF) bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). a) Comparison of Tris-Gly (Laemmli; top) and Bis/Tris SDS gels (bottom). Standard SerpinB1 species were generated by reacting rSerpinB1 with increasing elastase. The molecular forms separated on bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)-amino-Tris (Bis-Tris) gels are the 42-kDa active SerpinB1 (bottom, left lane), 66-kDa SerpinB1–protease complex, partially degraded complex (#) and 38-kDa cleaved SerpinB1. b) Bis-Tris immunoblots of patient BALF. In the top panel, lanes 1–9 contain coded BALF specimens of CF patients. All but specimens 6 and 7 are elastase positive. Lane 10 contains the single disease-control specimen (out of 11 analysed) that had SerpinB1 detectable by this method. Std: mixture of sandards. The major species in CF BALF is the 38-kDa cleaved SerpinB1 with variable minor amounts of the 66-kDa complex. A degradation product is seen in BALFs 2, 3 and 9. The bottom panel shows a repeat analysis to verify size (38 kDa) of the species in CF patient BALF. Groups of recombinant SerpinB1 (Std), Std mixed with CF BALF and CF BALF sample alone were analysed. Lanes 2 and 3 contain a pool of four CF samples (two elastase-positive and two –negative sample), lanes 5 and 6 contain the CF BALF run in lane 4 of the top panel), lanes 8 and 9 contain an elastase-positive CF BALF, and lanes 11 and 12 contain the CF BALF sample run in lane 8 of the top panel.