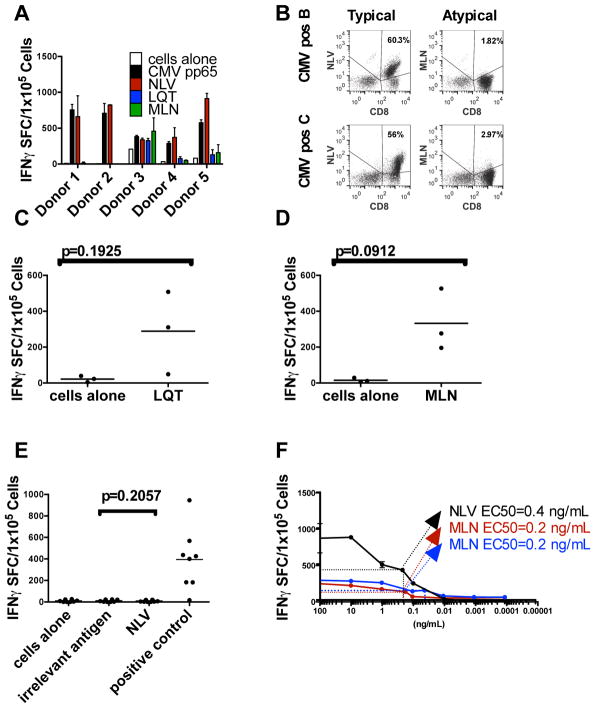
Figure 3. Recognition of typical and atypical epitopes by CMV-seropositive donors.
(A) Virus-specific T-cells from five CMV-seropositive donors were expanded against the entire CMVpp65 antigen. After three stimulations, they were tested for recognition of atypical (LQT, MLN) and typical (NLV) epitopes as determined by the IFN-γ ELISPOT assay and (B) pentamer analysis. (C and D) T-cells from CMVpos donors were stimulated three times with DCs pulsed with the indicated peptide. The number of cells that secrete IFN-γ in response to stimulation with LQT (C) or MLN (D) peptide is shown on approximately day 21 of culture. Gray bars indicate mean n values. (E) Failure to generate NLV-specific T-cells from CMV-seronegative donors (grey diamonds, n=3) or CB (black diamonds, n=5). T-cells were stimulated with DCs pulsed with the peptide NLV in the absence of other peptides. After three stimulations, the resulting cells were tested for their ability to recognize NLV. Grey bars indicate mean values. SEB, Staphylococcal enterotoxin B. (F) T-cells from CMV-seropositive donors were stimulated as above with the peptide NLV and tested by limiting dilution for the mean one-half effective concentration (EC50). Error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of triplicate wells; a representative result is shown (see table 1 for the avidity of other lines). (G) T-cells from CMV-seropositive donors were stimulated with the atypical peptide MLN and tested by limiting dilution to determine the EC50. (H) T-cells from CB and CMV-seronegative donors were stimulated with the atypical peptide MLN and tested by limiting dilution to determine the EC50. Values shown in panels EG are the numbers of spots above background.