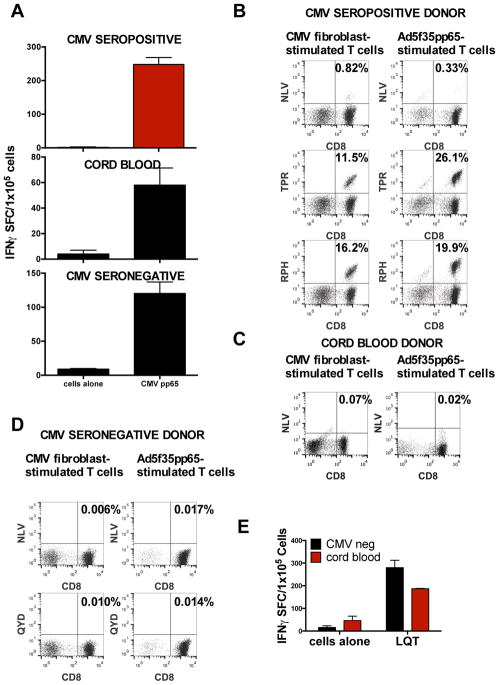
Figure 4. Epitope recognition by T-cells stimulated with live CMV.
(A) Comparison of response to CMVpp65 by T-cells from HLA-A2+ CMV-seronegative donors, CMV-seropositive donors, and CB. The T-cells were stimulated with CMV-infected HLA-A2+ fibroblasts that were cocultured with DCs and then tested with an IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. Mean ± SD values from triplicate wells are shown. (B) Typical epitope (HLA-A2-restricted NLV, B7-restricted TPR and RPH, or A24-restricted QYD) recognition of cells from a CMV-seropositive donor line stimulated with CMV-infected fibroblasts or an adenoviral vector expressing CMVpp65 as described. (C) Typical epitope recognition by CB T-cells stimulated with CMV-infected fibroblasts or the adenoviral pp65 vector. (D) Typical epitope recognition by CMV-seronegative T-cells stimulated with CMV-infected fibroblasts or the adenoviral pp65 vector. (E) Atypical epitope recognition by CB-derived T-cells generated with CMV-infected fibroblasts. Pool 13 contained the atypical epitope LQT.