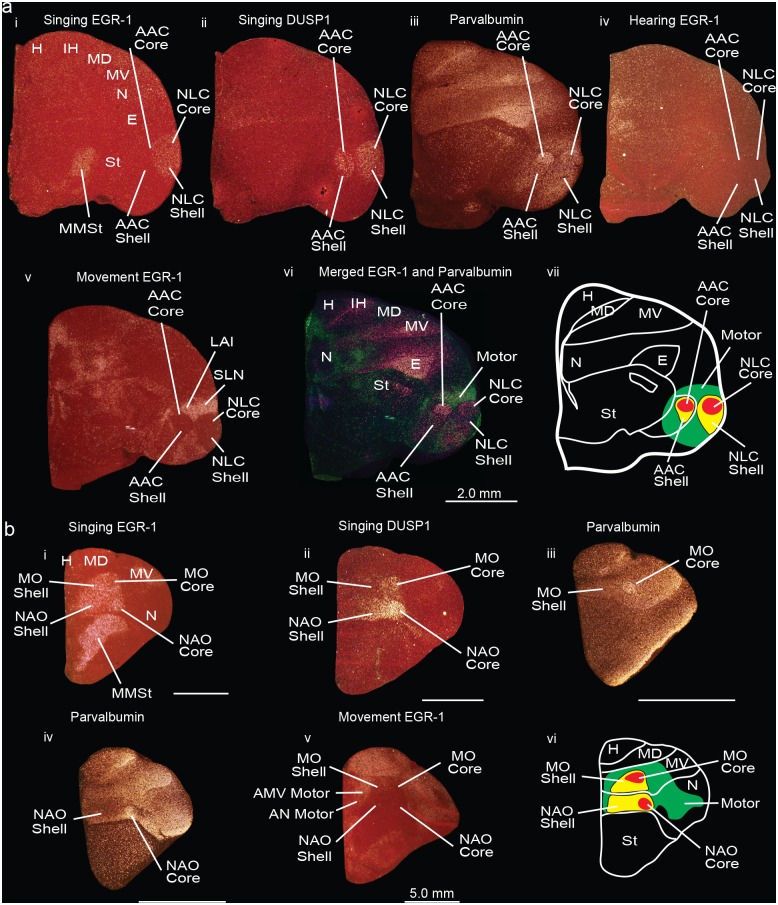
Fig 4. Darkfield photomicrographs showing PVALB, EGR-1, and DUSP1 mRNA expression in the budgerigar brain in different behavioral states.
(a) Darkfield images of EGR-1, DUSP1, and PVALB mRNA expression in sections containing song nuclei of the posterior vocal pathway. (i) Vocalizing-induced EGR-1 expression within the NLC core and shell; EGR-1 mRNA expression is not distinguishable in AAC in this animal because of lower amount of vocalizing behavior; (ii) Vocalizing-induced DUSP1 expression in the NLC and AAC core and shells; (iii) PVALB specialized expression in the NLC and AAC core and shells, as well as adjacent motor areas around the shells; (iv) Lack of hearing-induced EGR-1 expression in the NLC and AAC in a silent bird; (v) Movement-induced EGR-1 expression in regions around the NLC shell and AAC shell song nuclei; (vi) Merged images of movement-induced EGR-1 expression (green) which overlaps with the motor part of the shell region defined by PVALB expression (purple), and the PVALB-defined core and shell regions of NLC and AAC (purple); (vii) Schematic diagram showing regions of song nuclei cores (red) and shells (yellow), and adjacent motor shell regions (green). (b) Darkfield photomicrographs of PVALB, EGR-1, and DUSP1 mRNA expression in coronal brain sections containing anterior vocal pathway song nuclei. (i) Vocalizing-induced EGR-1 expression in the MO and NAO core and shell song nuclei, and the MMSt song nucleus; (ii) Vocalizing-induced DUSP1 expression in the MO and NAO core and part of shell song nuclei; (iii) PVALB expression in the MO core; (iv); PVALB expression in the NAO core; (v) Movement-induced EGR-1 expression in the areas surrounding the MO and NAO shells; (vi) Schematic diagram showing regions of the MO and NAO core (in red) and shell (yellow) song nuclei, and motor regions surrounding them (green). Sections are in the coronal plane; medial is to the left, dorsal is top. Some sections are compiled from the same animals of studies conducted in Horita et al. [45] (panels a-i to ii, b-ii), Jarvis and Mello [24] (a-iv, b-i), and Feenders et al. [35] (panels a-v, b-v). See Table 3 for nomenclature. See list for Abbreviations.