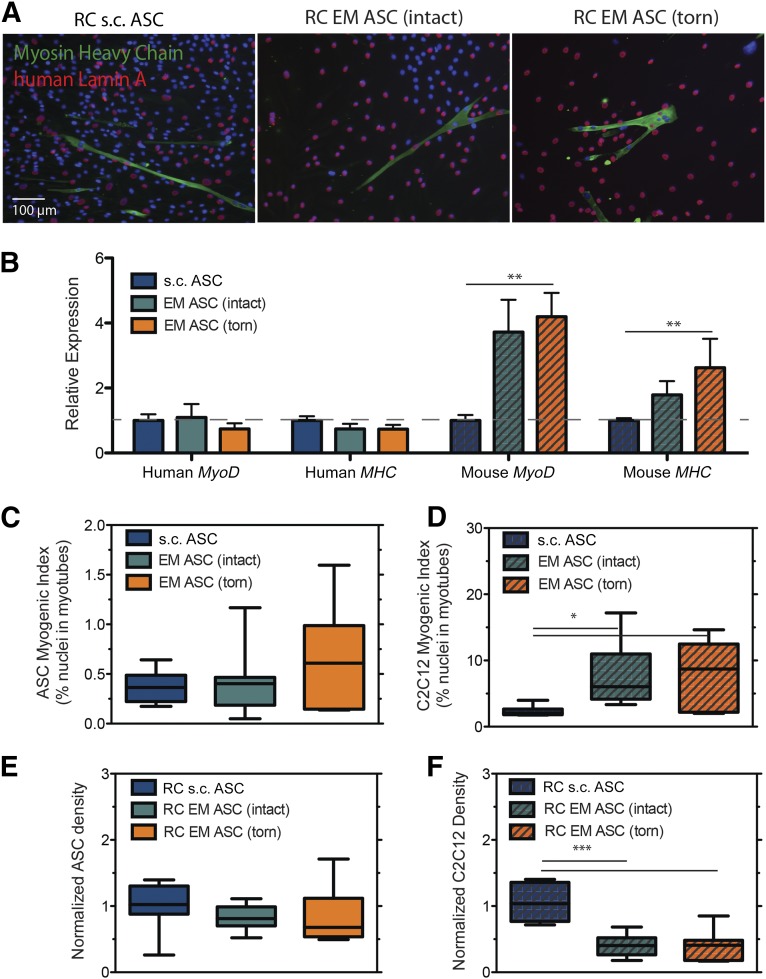
Figure 7.
Epimuscular ASCs affect C2C12 proliferation and fusion in coculture. (A): Immunofluorescent images of cross-species (human ASC and murine C2C12) coculture. ASC nuclei are identified using a human-specific antibody to lamin A (red), and myotubes are identified by myosin heavy chain (MHC; green). Myotubes were identified containing both human and mouse nuclei in all cultures. No myotubes were identified containing only human nuclei. (B): Quantification of species-specific isoform expression of MyoD and MHC. Gene expression values were normalized to s.c. ASC average expression. (C): Plot of the ASC myogenic index, defined as the percentage of total lamin A-positive nuclei in MHC-positive structures. (D): Plot of the C2C12 myogenic index, defined as the percentage of total lamin A-negative nuclei in MHC-positive structures. At the end of the culture period, the density of ASCs (E) and the density of C2C12 cells (F) was assessed from cocultures. Culture densities were normalized to the s.c. ASC average. ∗, p < .05; ∗∗, p < .01; ∗∗∗, p < .001.