Figure 3.
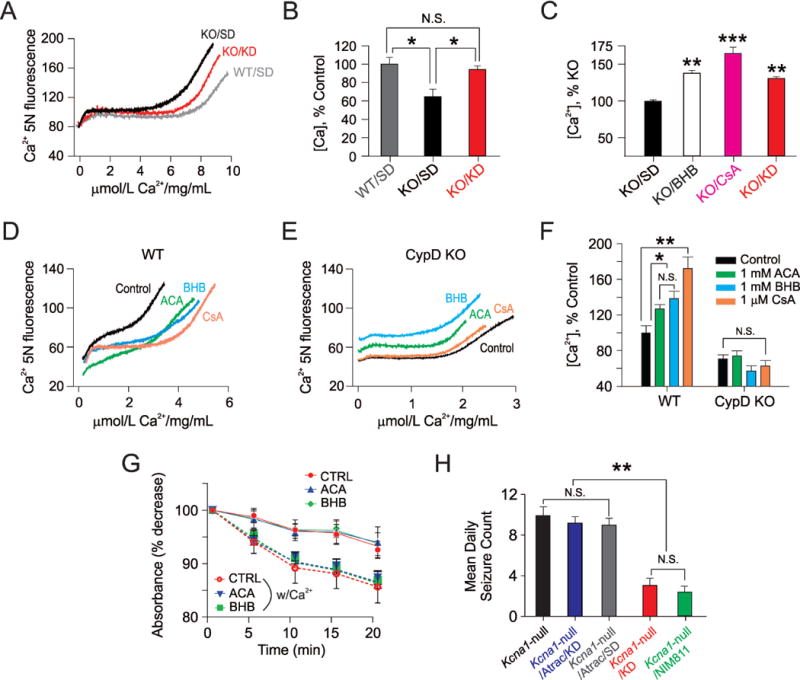
The cyclophilin D (CypD) subunit of the mitochondrial permeability transition (mPT) complex is required for functional neuroprotection by ketone bodies (KB). (A and B) Ketogenic diet (KD) treatment increases mPT threshold in Kcna1-null (KO) mice. Isolated brain mitochondria from wild-type (WT) C3H mice were able to accumulate more Ca2+ than mitochondria prepared from KO mice. (A) Representative spectrofluorometric traces indicating the capacity of mitochondria to sequester Ca2+ administered through bolus injections. Two weeks of KD treatment increased the capacity for Ca2+ uptake and fully restored mPT threshold in KO mitochondria. (B) Summary bar graphs of the different treatment groups. Each sample comprised pooled mitochondria from 3 mice. * p <0.05, n=4 per group. (C) β-hydroxybutyate (BHB) increases mPT threshold in acutely isolated cortical mitochondria from Kcna1-null (KO) mice. Graph indicates the different treatment groups normalized to KO mitochondria. For comparison, the mPT threshold in mitochondria from ketogenic diet (KD)-treated KO mice is shown (black bar). Each bar indicates the mean ± S.E.M, and each mitochondrial sample tested came from a single mouse. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferonni correction, n=4–5 samples per group. (D and E) Traces depicting thresholds for Ca2+-induced mPT in acutely isolated hippocampal mitochondria from B6 wild-type mice (D) and age-matched CypD-null mice (E). For these experiments, calcium was administered through micro-infusion. In CypD-null mice, neither BHB nor ACA – each 1 mM – were effective in raising the mPT threshold. Cyclosporin A (1 μM) was also not effective in altering Ca2+-induced mPT. (F) Summary bar graphs showing the mean ± S.E.M. of mPT thresholds for the various treatment groups. Note: the thresholds for calcium-induced mPT differed not only amongst the treatment groups, but also varied as a function of different background strain, and whether mice were wild-type or null mutants. (G) Ca2+ -induced swelling of control mitochondria with or without pre-incubation of 1 mM ACA and 1 mM BHB in control C57Bl6 mice. These experiments were performed under de-energized conditions and with a Ca+2 ionophore in order to equilibrate this cation across the mitochondrial inner membrane. Ca+2 (200 μM)-induced swelling increased in control, as well as ketone-treated samples. ACA and BHB treatment did not inhibit Ca+2-induced mitochondrial swelling as shown. Data represent n=5 animals in each group and samples were measured in two replicates per animal. (H) Atractyloside reverses the anti-seizure effects of the KD. Mean daily seizure frequencies over a 3-day recording period in Kcna1-null mice after various two-week treatments – those administered: (1) a standard diet (SD) only; (2) a KD plus atractyloside (ATRAC) 30 mg/kg IP daily; (3) a SD plus ATRAC; (4) a KD only; and (5) the selective cyclophilin D (CypD) inhibitor NIM811, 10 mg/kg IP daily. NIM811 resulted in an anti-seizure effect similar to what was observed with either the full KD or KB (see Figure 1). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test; **, p <0.01. N=8–9 per group. For panels (B, F, G and H), data points reflect the mean ± S.E.M.
