Figure 4.
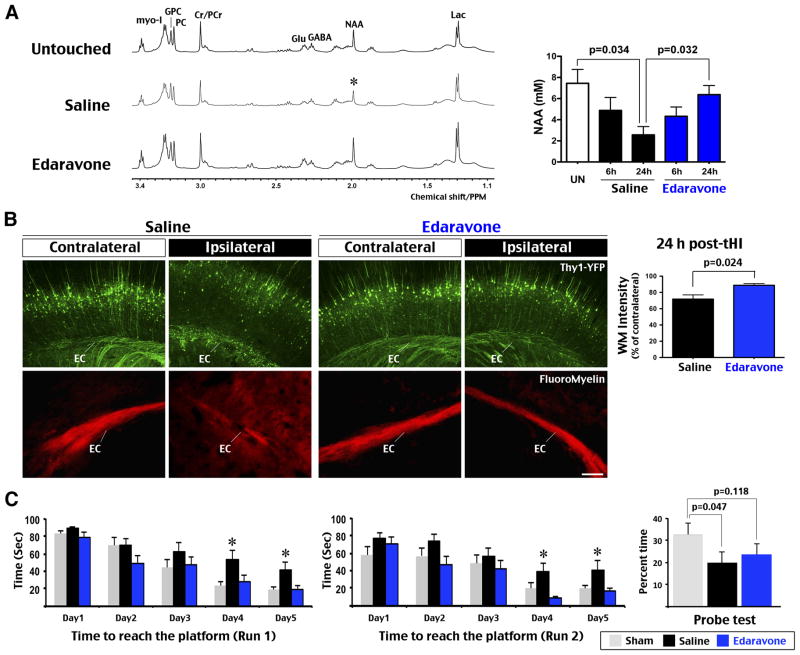
Edaravone prevented tHI-induced alteration of brain metabolites and learning deficits. A, Representative HRMAS NMR spectra of the cortical tissue from brain slices of untouched, tHI-injured and saline- versus Edaravone-treated mice at 24 h recovery. The brain NAA (N-acetyl-aspartate) level was reduced to a similar degree in saline- and Edaravone- treated mice at 6 h post-tHI (n=4 each), but more diminished in saline-treated mice at 24 h recovery (n=3 for untouched and each treatment). Shown are p-values determined t-test. Labeled are the peaks for Lac (lactate), GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), Cr/PCr (creatine and phosphocreatine), PC (P-choline), GPC (glucocerphosphocholine), Glu (glutamate), and myo-I (myo-inisitol). B, Thy1-YFP mice received Edaravone treatment showed less white-matter damage than those received saline (n=6 for each). Shown is the quantification of Thy1-YFP fluorescence in the ipsilateral external capsule (p=0.024 by t-test, n=4 each). Fluoromyelin stain showed attenuated and diffused signals in the ipsilateral external capsule (EC) in mice received the saline treatment (n=4 each). C, Effects of Edaravone on learning-memory preservation were assessed by the latency to location in run 1 (reference memory) and run 2 (working memory) in Morris water maze in 5 consecutive day, and the probe test on day 8. Saline-treated mice showed longer latency than sham and Edaravone-treated mice in day 4 and 5 (*p<0.05 by post-hoc LSD multiple comparison test, n=12 for each group), and less time spent in the probe quadrant than sham-treated mice on day 8 (p=0.047 by t-test). Values are mean ± standard error. Scale bar: 100 μm.