Fig. 8.
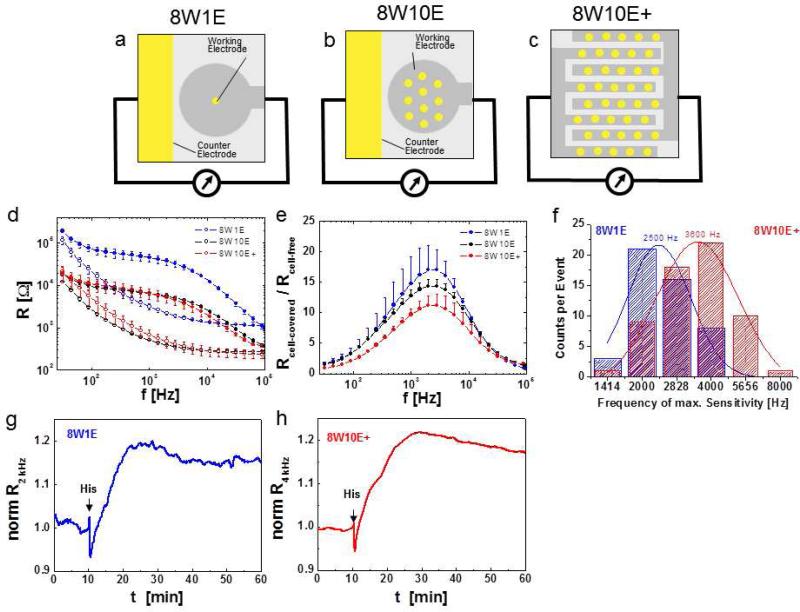
Electrode layouts influence sensitivity of ECIS measurements. a – c Schematic top view of coplanar electrode layouts of one chamber/well of a 8W1E (8 wells, 1 electrode/well), b 8W10E (8 wells, 10 electrodes/well) and c 8W10E+ (similar electrical behavior as 8W10E) arrays (yellow: gold electrode surfaces, grey: insulating polymer). d Resistance versus frequency spectra for 8W1E, 8W10E and 8W10E+ electrodes. The respective cell-free (traces with open circles) and cell-covered (confluent HDMEC; traces with closed circles) spectra (average and SD from 8 wells) are shown. e Rcell-covered / Rcell-free as a function of frequency showing different sensitivities of different electrode layouts. f Distribution of maximum sensitivity frequency for 49 (on 8W1E), 61 (on 8W10E) individual confluent HDMEC cell layers (from different isolations and passage numbers) after 4 days of culture on either 8W1E (blue) or 8W10E+ (red) electrodes. g, h Resistance profiles of confluent HDMEC cell layers upon histamine stimulation (arrows) on g 8W1E and h 8W10E+ ECIS array, plotted as normalized resistance (normalized to resistance values before histamine addition) at their respective maximum sensitivity frequency.