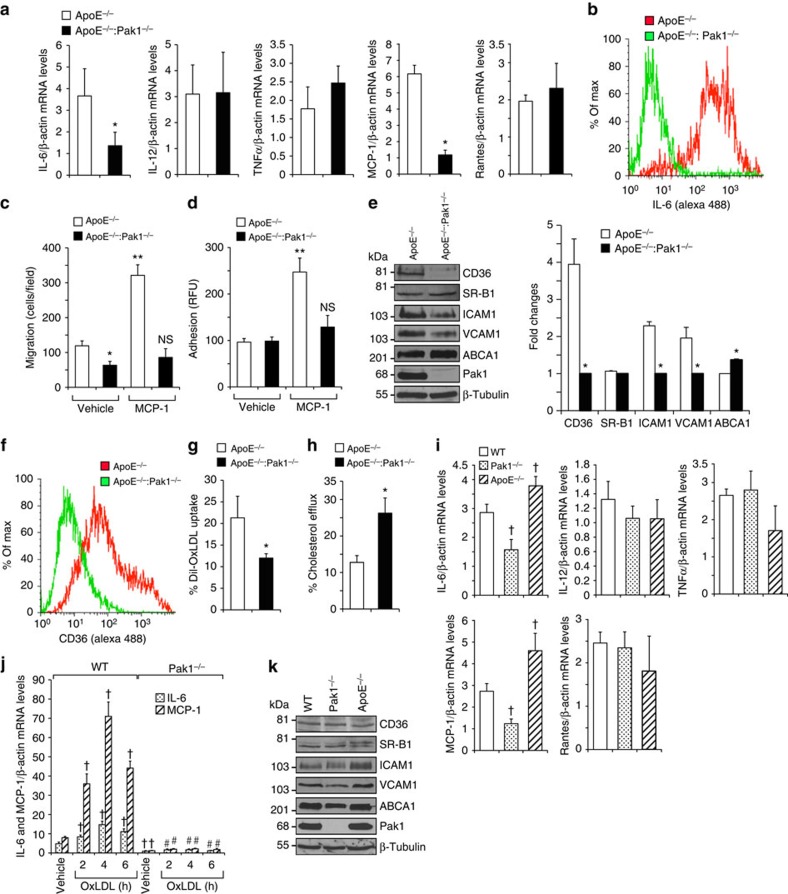
Figure 4. Pak1 deficiency affects macrophage function.
(a) RNA from peritoneal macrophages of ApoE−/− and ApoE−/−:Pak1−/− mice fed with WD for 16 weeks was analysed by qRT–PCR for the indicated cytokines and chemokines. (b) FACS analysis of IL-6-positive peritoneal macrophages from ApoE−/− and ApoE−/−:Pak1−/− mice fed with WD for 16 weeks is shown. Peritoneal macrophages isolated from the mice described in a were subjected to MCP-1 (50 ng ml−1)-induced migration (c) and adhesion (d). (e) Extracts of peritoneal macrophages isolated from the mice described in a were analysed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. Bar graph in e represents the quantification of three western blottings each from a group of two pooled arteries. (f) FACS analysis of CD36-positive peritoneal macrophages isolated from the mice described in a is shown. Peritoneal macrophages from ApoE−/− and ApoE−/−:Pak1−/− mice fed with WD for 16 weeks were analysed for Dil-OxLDL uptake (g) and cholesterol efflux (h). (i) RNA from peritoneal macrophages of WT, Pak1−/− and ApoE−/− mice fed with CD was analysed by qRT–PCR for the indicated cytokines and chemokines. (j) Peritoneal macrophages of WT and Pak1−/− mice fed with CD were treated with OxLDL (10 μg ml−1) for the indicated time periods and RNA was isolated and analysed by qRT–PCR for IL-6 and MCP-1 levels. (k) Extracts of peritoneal macrophages isolated from the mice described in i were analysed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. Data were presented as mean±s.d. and assessed by Student's t-test. *P<0.01 versus ApoE−/− mice (n=6); **P<0.01 versus vehicle control; †P<0.01 versus WT mice (n=6) or WT+vehicle, #P<0.01 versus WT mice+OxLDL (n=6). NS, not significant compared with vehicle control.