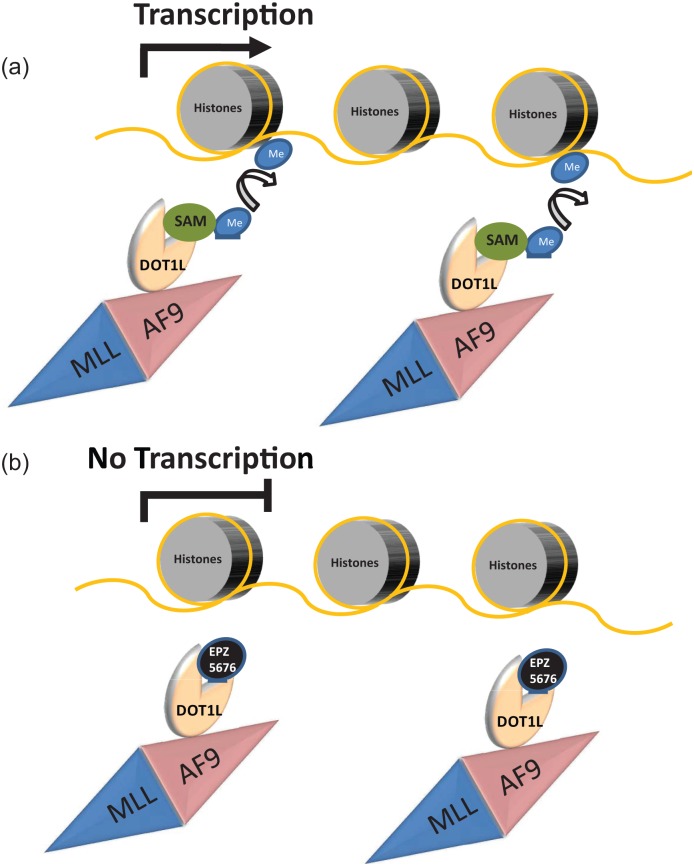
Figure 2.
Model for the mechanism of action of DOT1L inhibitors.
The lysine methylase disruptor of telomeric silencing 1 like (DOT1L) is known to interact with several fusion partners of MLL translocations, such as AF4, AF9, AF10 and ENL. DOT1L interaction with AF9 leads to its aberrant recruitment to MLL-AF9 fusion target genes. At these target sites, DOT1L methylates lysine 79 of histone 3 (H3K79) using S-(5′-adenosyl)-l-methionine (SAM) as a donor of methyl (Me) groups. H3K79 methylation is known to be an activating mark which facilitates transcription of MLL target genes (a). EPZ-5676 mimics SAM binding to DOT1L, leading to inhibition of its methylase activity, reduction of H3K79 methylation at MLL-AF9 target genes and transcriptional suppression of MLL-AF9 oncogenic program (b).