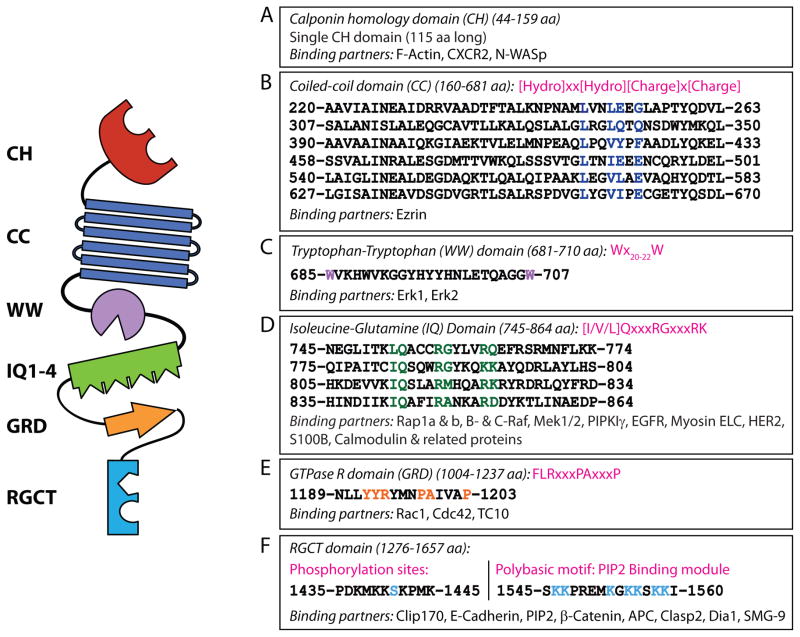
Figure 2. Protein structure of and specific domain-interacting partners of IQGAP1.
IQGAP1 is a 190 kDa (1657 amino acid) protein that contains six distinct protein-interacting domains. The domains and known interacting proteins are shown as well as amino acid sequences (mouse). A) The calponin homology (CH) domain binds the chemokine receptor, CXCR2, and regulates the actin cytoskeleton by binding N-WASp and polymerized filamentous actin (F-actin). B) Six coiled-coil (CC) regions, comprised of highly conserved amino acid repeats, comprise the coiled-coil (CC) domain which binds Ezrin. C) Erk1/2 are recruited to the WW domain. D) The Isoleucine/glutamine-containing (IQ) domain is a binding domain for multiple proteins that include components of MAPK signaling (Rap1a, Rap1b, B-Raf, C-Raf, Mek1 and Mek2), phosphoinositide signaling (PIPKIγ), calcium signaling (S100B and Ca2+-independent interaction of calmodulin and its related proteins), as well as cytoskeletal components (myosin ELC) and cell surface receptors (EGFR and HER2). E) The Ras-GAP domain (GRD) does not function as a GTPase Activating Protein (GAP) but does interact with small GTPases Cdc42, Rac1, and TC10. F) The Ras-GAP C-terminus domain (RGCT) interacts with microtubule-binding proteins CLIP-170 and Clasp2, as well as membrane-resident proteins such as β-catenin, E-cadherin, and APC. The RGCT domain also contains two phosphorylation sites (Ser1441 and Ser1443) of IQGAP1 as well as a polybasic region which binds PIP2. Other proteins previously shown to interact with IQGAP1 (Akt, mTORC1, exorcist, Sec3/8, Lis1, Menin, SMG-2, and Disheveled) are not depicted.