Figure 3. IQGAP1 plays a critical role in actin polymerization.
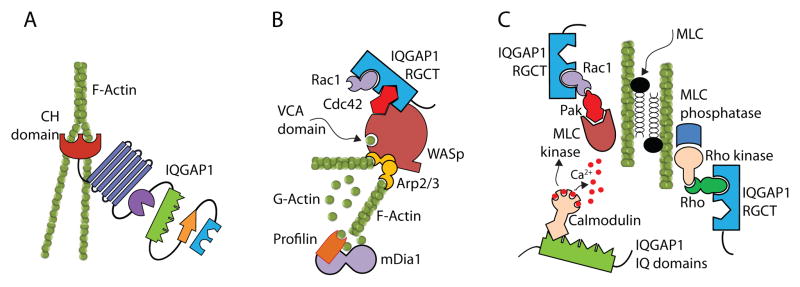
IQGAP1 can regulate actin polymerization by at least three different mechanisms. A) RGCT domain of IQGAP1 can Cdc42 or Rac1 is recruited by autoinhibited WASp through ‘Cdc42-interactive-binding’ (CRIB) motif. This causes a conformational change in the C-terminal verprolin homology domain and central acidic (VCA) region of WASp allowing globular actin to bind through an electrostatic steering mechanism. In addition, IQGAP1 transiently protects Cdc42-GTP in its activated state, reducing its GTP hydrolysis. By delaying the hydrolysis of WASp-bound Cdc42-GTP, IQGAP1 stabilizes the VCA domain of WASp. This sustains the interaction with Arp2/3 and globular actin, promoting the polymerization and branching of actin. B) The CH domain of IQGAP1 interacts with polymerized F-actin. a single N-terminal CH domain facilitates actin polymerization by cross linking filaments into interconnected bundles. C) RGCT domain of IQGAP1 can regulate polymerized actin filament through myosin light chain (MLC) in a co-ordinated effort of MLC kinase and MLC phosphatase by PAK and Rho, respectively. In addition, MLC kinase function can be regulated by IQGAP1-bound calmodulin.
