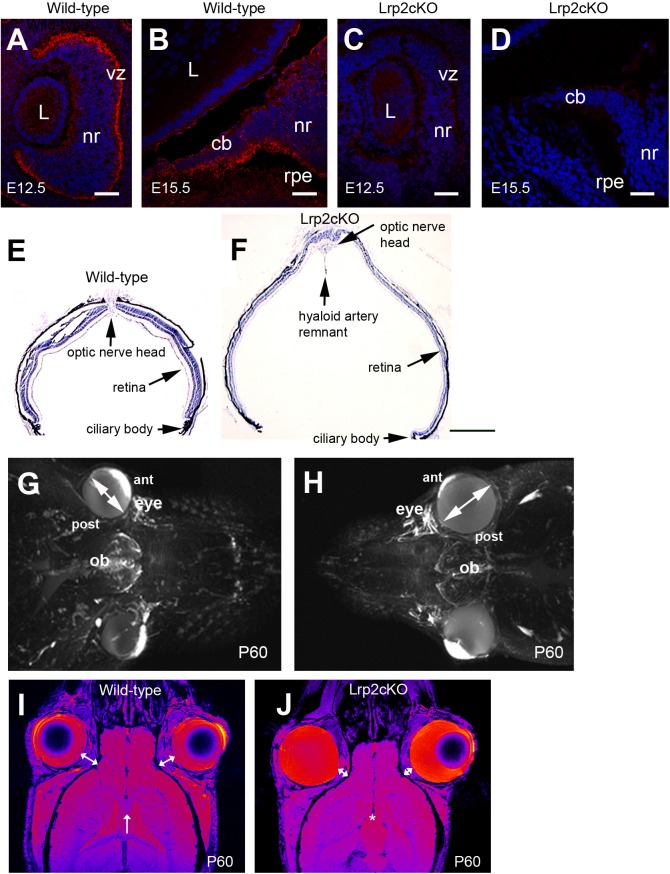
Fig 1. Lrp2-deficient eyes are abnormally enlarged.
Sagittal cryosections through the developing eye (A-D). Lrp2 is expressed in the developing neuroretina (nr) at E12.5 (A). From E15.5 onward the signal is restricted in the lens (L) facing inner layer of the ciliary body (cb) epithelium, a low expression is also seen in the outer layer of the CB and in the retinal pigmented epithelium (rpe) (B). Loss of Lrp2 signal in Lrp2 FoxG1.cre-KO mutants at E12.5 and E15.5 (C, D). Sagittal cryosections of control and mutant retinas at P60 showing retinal thinning and the presence of a posterior staphyloma in the mutant (E, F). Reconstruction of the mouse face using MRI at P60 (G, H). The Lrp2 FoxG1.cre-KO mutants display bilateral eye enlargement, through the anterior-posterior axis and the equatorial diameter (double headed arrows in G, H). Horizontal MRI images showed that the retrobulbar space, between the orbit and the eyeball, (double-headed arrows in I, J) is decreased in Lrp2 FoxG1.cre-KO mutants. The corpus callosum (arrow in I) is not formed in the mutants (asterisk in J). (vz) ventricular zone. Scale bars: 25 μm in A-D; 600 μm in E, F.