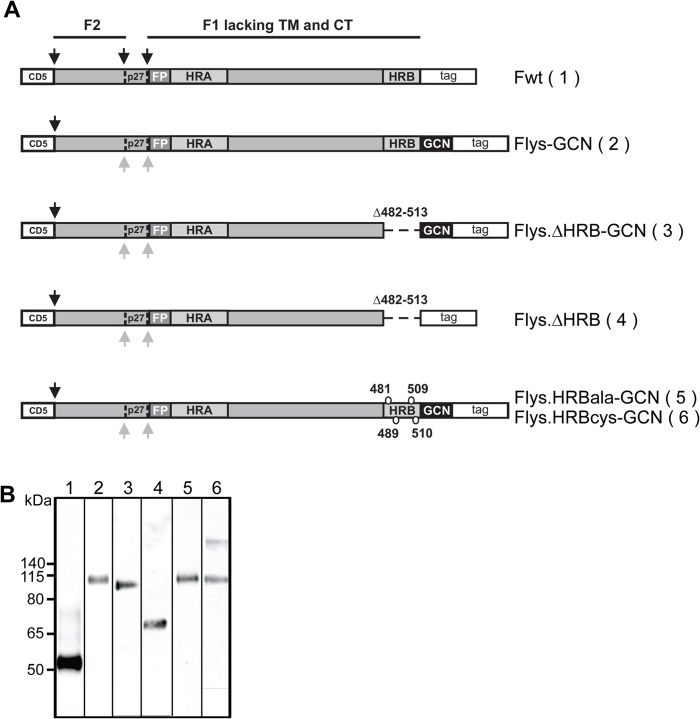
Fig 4. Schematic representation of the different recombinant soluble RSV F protein constructs.
(A) RSV F ectodomains (amino acid 26–513) lacking the transmembrane domain (TM) and cytoplasmic tail (CT) were genetically fused to a CD5 signal peptide (CD5) and to a carboxy-terminal triple Strep tag II (tag). When indicated a GCN4 trimerization motif [34] and a LysM linker [35] immediately downstream of the RSV F ectodomain were added (indicated by GCN). The F2 and F1 subunits of F are indicated, as well as the p27 peptide (P27) that is released after furin cleavage. Protease cleavage sites are indicated by black arrows. Grey arrows indicate mutated furin cleavage sites. The approximate location of the fusion peptide (FP), heptad repeat A (HRA) and B (HRB) is also shown. The residues substituted in HRB by alanines or cysteines in Flys.HRBala-GCN and Flys.HRBcys-GCN, respectively, are indicated. The amino acids deleted in the F proteins that lack HRB are also indicated. (B) SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of recombinant soluble F proteins. Purified F proteins Fwt (lane 1), Flys-GCN (lane 2), Flys.∆HRB-GCN (lane 3), Flys.∆HRB (lane 4), Flys.HRBala-GCN (lane 5), Flys.HRBcys-GCN (lane 6) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting. Prior to SDS-PAGE analysis, the samples were resuspended in LSB containing 5% ME and heated at 96°C for 5 minutes. The size of the molecular mass markers (in kDa) is shown on the left side.