Fig. 3.
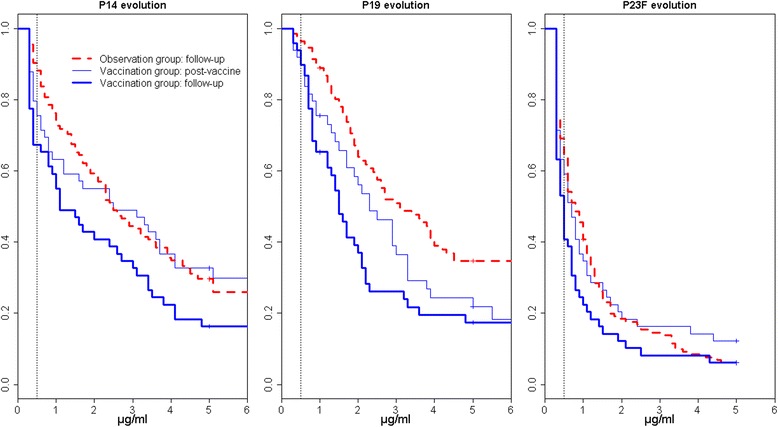
Evolution of serology to vaccine serotypes 14, 19 and 23F in 49 patients immunized with the 23-valent polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccine compared with 135 patients observed after 4–8 weeks and after 1 year. Reverse cumulative distribution curves of specific serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) against serotypes 14, 19 and 23F in patients immunized 4–8 weeks after vaccine (thin blue lines) and after 1 year (bold blue lines) compared with patients observed after 1 year (dotted red lines). Reverse cumulative distribution function takes into account censored values obtained by real-time enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [28]. Median (95 % confidence interval) specific IgG titers to pneumococcal serotype 14 decreased from 2.5 (1.2–4.1) μg/ml 4–8 weeks after immunization to 1.1 (0.8–3.0) μg/ml after 1 year (p = 0.001 by from paired Prentice–Wilcoxon test for censored paired data), to serotype 19 from 2.3 (1.7–3.3) to 1.5 (1.2–2.1) μg/ml (p = 0.009) and to serotype 23F from 0.7 (0.5–1.1) to 0.5 (0.4–0.7) μg/ml (p = 0.005). In patients observed, median (95 % confidence interval) IgG values after 1 year were 2.5 (2.1–3.4) μg/ml to serotype 14, 3.1 (2.5–4.2) μg/ml to serotype 19 and 0.8 (0.6–1.0) to serotype 23F
