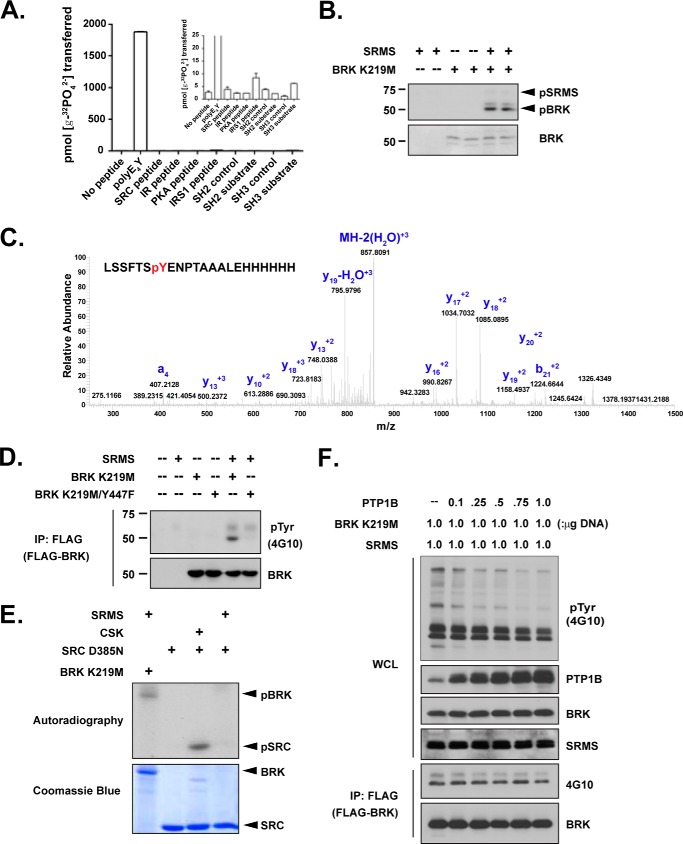
FIGURE 5.
SRMS, but not CSK, phosphorylated the C-terminal tyrosine of BRK. (A) The activity of purified WT SRMS protein was measured toward various peptides using the phosphocellulose paper binding assay. The inset shows an expanded range. (B) Purified SRMS and kinase-inactive BRK K219M proteins were incubated for 30 min at 30 °C in the presence of γ-32P-ATP. The reactions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and proteins were detected by autoradiography (top panel) or Coomassie Blue staining (lower panel). (C) Kinase-inactive BRK K219M was incubated either with or without SRMS under phosphorylation conditions. Following kinase reactions, proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. Bands corresponding to BRK were excised, digested with trypsin, and analyzed by LC-MS. The LC peaks corresponding to the peptide fragments containing Tyr-447 in SRMS-treated BRK fractions were further analyzed by MS/MS. (D) The indicated constructs were expressed in SRC/Yes/Fyn−/−/− (SYF) fibroblasts. Proteins were immunoprecipitated from whole cell lysates with anti-FLAG and analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) In vitro reactions were performed with SRMS, CSK, and the kinase-inactive forms of SRC and BRK in the presence of γ-32P-ATP. The reactions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and proteins were detected by autoradiography or Coomassie Blue staining. (F) FLAG-BRK K219M, SRMS, and increasing amounts of PTP1B cDNA were co-transfected in 293T cells, as indicated. BRK K219M was immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG, followed by Tyr(P) (4G10) blotting.