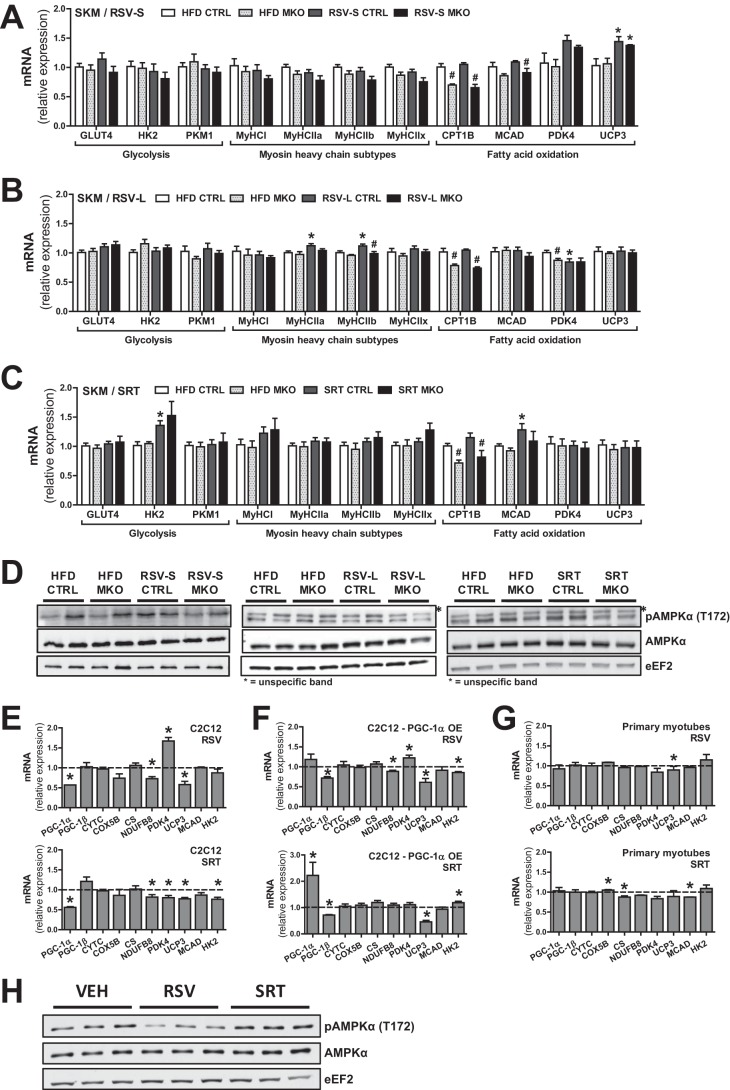
FIGURE 3.
RSV and SRT treatment elicit minor transcriptional effects in skeletal muscle cells. A–C, mRNA levels of genes involved in glucose uptake and glycolysis, myosin heavy chain (MyHC) subtypes, and fatty acid β-oxidation in SKM relative to Polr2a (RSV-S and RSV-L) or Hprt (SRT) (n = 5–8/group). D, representative immunoblots of AMPKα total protein and AMPKα phosphorylation (Thr-172) in SKM (n = 6/group). E–G, mRNA levels of the indicated genes normalized to vehicle group (dashed line) in C2C12 myotubes (E), C2C12 myotubes overexpressing (OE) PGC-1α through adenoviral transduction (F), or primary mouse myotubes (G). All were treated for 24 h with either 50 μm RSV or 10 μm SRT, relative to Tbp. H, immunoblots of AMPKα total protein and AMPKα phosphorylation (Thr-172) in C2C12 mouse myotubes treated for 24 h with either 50 μm RSV or 10 μm SRT1720. Bars, means ± S.E. (error bars). Significant differences (p < 0.05) between CTRL and PGC-1α MKO mice are indicated (#) as well as significant differences between untreated and treated groups (*). PKM1, pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme 1.